What is a wormhole? Wormhole is one of the first generation cross-chain support platforms. And it is a bridge used by many people, although the technology is a bit complicated and not optimized in terms of security. So what is Wormhole? How does it solve the above problem? Let’s find out in this article!
To understand more about Wormhole and how it works, you can read the following articles:
- What is Axelar Network (AXL)? Axelar Network Cryptocurrency Overview
- What is LayerZero? LayerZero Cryptocurrency Overview
- Working Mechanism of LayerZero, a New Generation Multi-Chain Bridge
- What is Portal Finance? Overview of Cryptocurrencies Portal Finance
- Bridges: Design, Trade-offs, and Opportunities
What is Wormhole?
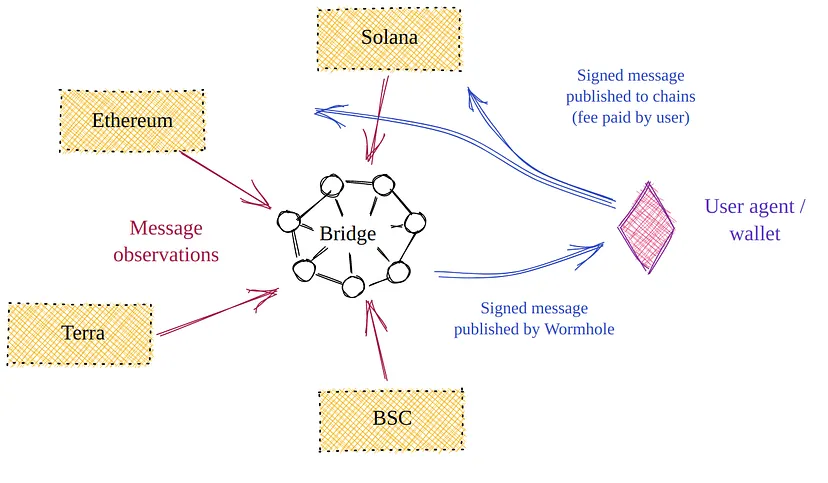
Wormhole is a generic message passing protocol connected to many chains including Ethereum, Solana, BNB Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, Algorand, Fantom, Karura, Celo, Acala, Aptos and Arbitrum.
Wormhole does this through Core Bridge contracts mounted on chains. Emission of messages from a chain is observed by the network of Guardians nodes and verified there. Once verified, this message is sent to the target chain for processing.

Wormhole is the basis for building cross-chain dApps. Thanks to the message relay technology and toolset provided by Wormhole. dApps that have been built on other chains can also link Wormhole for Multichain development or support multi-chain governance.
Use Lock/Mint and Burn/Unlock mechanisms to transfer assets across the chain. Specifically, Wormhole will lock the original token in the first chain and issue a new token as a wrapper in the destination chain. It is also a security issue. In fact, Wormhole’s Portal Bridge was attacked by Hackers on February 2, 2022. Hackers exploited a protocol vulnerability to mint 120k ETH encased in Wormhole on the Solana network.
On Wormhole nUsers can interact with xDapps (cross-chain decentralized applications) to transfer xAssets (cross-chain assets) between networks or access xData (cross-chain data) to provide services on the network for them.
In addition to Wormhole’s messaging protocol, there are two specific applications that help centralize liquidity for xAssets. Portal Token Bridge and Portal NFT Bridge provide a standard message format for transferring tokens and NFTs across the Wormhole bridge.
Some outstanding examples of xDapps:
- Cross Chain Exchange: Using Portal developers can build an exchange that allows deposits from any chain with a Wormhole connection, significantly increasing the liquidity with which their users can interact. Users can deposit ETH from Ethereum directly into an application running on Solana, tAll developers have to do is integrate the Wormhole SDK into their user interface.
- Cross Chain Governance App: With all NFT collections on different networks. If a group of these collections on different networks want their owners to vote on a combined proposal, they can use a Wormhole to transfer all the votes from other chains to the voting chain.
- Cross Chain Game: A game can be built and played on one functional network like Solana, and its rewards issued as NFTs on another network, such as Ethereum.
Some new concepts in Wornhole:
- Portal Token Bridge: MA set of smart contracts that are custodial funds on the source chain and issue corresponding wrapped assets on the target chain. DBuilt on the Wormhole protocol.
- VAA – Verifiable Action Approval: Messages emitted by contracts need to be verified by guardians before they can be sent to the target chain. Once a majority of guardians reach consensus, the message is encapsulated in a structure called a VAA that combines the message with the guardian’s signature to form a proof.
Mechanism of Action
Structure of Wormhole
Wormhole is composed of 3 main parts:
- Core Bridge Contract: LSmart contracts are deployed on chains. These contracts have two functions that developers can take advantage of. They can emit VAA and verify VAA. EmitVAA takes a block of structured binary data and publishes it for the Guardian network to read and observe. VerifyVAA takes the VAA and verifies the signatures on it match those of the registered guardians.
- Guardian: LThe observers (19 nodes) of the messages and sign the corresponding payloads. Each Guardian performs this step separately. Then combine the obtained signatures with other Guardians. The resulting set of independent observations forms a multi-signature representation of the evidence, i.e. a state that has been observed and agreed upon by the majority of the Wormhole network. These multi-signatures are called VAAs in Wormhole.
- Relayer: Lis a software that picks the signed VAA from the Wormhole network and sends it to the target chain. Relayers typically take a fee to cover gas costs when sending transactions to the target chain. Since the repeater does not perform any cryptographic functions on the VAA, it can run in an untrusted environment and cannot spoof the VAA.
Wormhole’s mechanism of action
Wormhole’s operating process is as follows:
1. A message issued by a contract running on chain A.
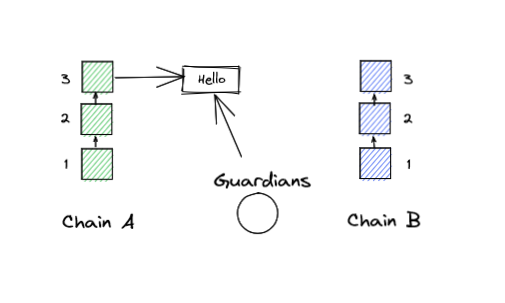
Messages can be emitted by any contract on chain A, and Guardians are programmed to observe all chains for these events. Here, Guardians are represented as a single entity to simplify the graphics but message observation must be done individually by each of the 19 nodes.
2. Synthesis of signatures.
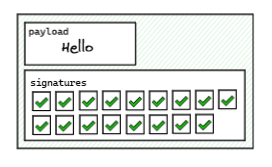
An independent guardian observes and signs the message. Once enough custodians have signed the notification, the collection of signatures is combined with the notification and metadata to create the VAA.
3. VAA is sent to the target chain.
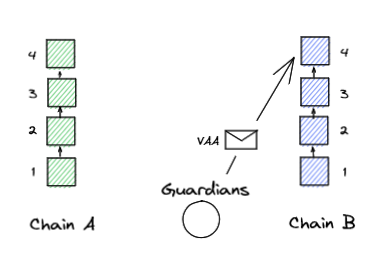
The VAA serves as proof that the defenders have jointly authenticated the existence of the message payload, to complete the final step, the VAA itself will be sent to the target chain to be processed by the contract. agree to accept.
Portal Bridge
Portal Bridge is a bridge built on Wormhole to support cross-chain transfers of assets or NFTs. And it also works according to the following 3 entities:
Transfers
To transfer tokens from network A to network B, Portal must lock the original token on chain A and mint the wrapped token on chain B. It is important that the tokens on A must be proven to be locked before minting can take place on B. To facilitate this process, chain A will lock the tokens and emit message indicating that the locking process is complete.
Attestation
The message passing process above is missing an important detail. Although the operation on chain B can trust the token lock message on chain A, it has no way of knowing what the token being locked actually is. To solve this problem, Portal Bridge supports token authentication. Chain A emits a message containing metadata about an address that chain B can store to find the name, symbol, and decimal precision of the token address.
Relayers
Token bridge conversion must be completed on the target chain, which will require payment of transaction fees in that chain’s native currency. Since many users making transfers may not have any currency, Wormhole provides a mechanism that allows Relayers to take the final step and pay fees on the user’s behalf.
This mechanism works by allowing users to specify a portion of tokens to be transferred as fees. When sending a VAA transfer, the contract will pay the fee to the Relayers instead of the user.
NativeSwap
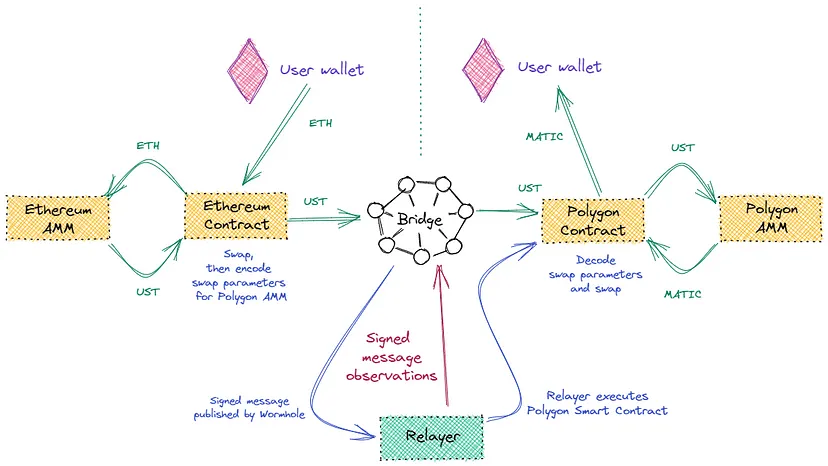
In early 2022, Wormhole introduced a cross-chain transfer mechanism through Stablecoin UST. But because of the collapse of UST in the middle of the year, this plan was canceled.
Development Roadmap
Updating…
Core Team
Updating…
Investors
Updating…
Tokenomics
Updating…
Exchanges
Updating…
Wormhole Information Channel
- Website: https://wormhole.com/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/wormholecrypto
- Medium:
Summary
Wormhole is one of the leading cross-chain platforms, with a large number of users. But there are still many risks of security breaches.
So I have clarified what Wormhole is? Wormhole cryptocurrency overview. Hope this article gives you a lot of useful knowledge!


