What is State Channel? State Channel is a Layer 2 solution that solves the scaling problem on Ethereum, especially in terms of transaction speed and transaction fees. So how does State Channel work, what are its advantages and disadvantages? Let’s find out together in the article below.
To better understand Layer 2 & State Channel, people can refer to some of the articles below:
- What is Layer 2? Complete Guide to Layer 2 Solutions
- What is Optimistic Rollup? Overview of Optimistic Rollup
- What is ZK Rollup? ZK Rollup Solution Overview
State Channel Overview
What are channels?
Channel is a P2P peer-to-peer channel that allows parties participating in the Channel to perform unlimited transactions and only post the final results to the Blockchain network. The channel will use cryptography to prove that the summarized data from the aggregation of previous transactions is valid. A Multisig Smart Contract (Multi-Signature Smart Contract) ensures transactions carefully recorded by participating parties are accurate.
Each Channel will be managed by a Multisig Smart Contract directly on Ethereum. To open a Channel, participants will deploy a Multisig Smart Contract and then deposit money. To be able to quickly and automatically off-chain transactions, participating parties sign a state update to initialize the Channel’s state.
To close a Channel, participants send the final state of the channel. Multisig Smart Contract will then return the funds according to the balance to the participating parties at the time of the final state of the channel. Channels in Blockchain are divided into two types: Payment Channel and State Channel.
What is Payment Channel?
Payment Channel is a technology that allows two users to conduct multiple transactions between them without having to post each transaction to the Blockchain. This helps reduce the load on the Blockchain and increase transaction speed. Payment Channel operates as a two-way ledger maintained by two users. When the channel is opened, each user will lock a certain amount of money into a smart contract on the Blockchain. They can then carry out transactions between themselves without having to post those transactions to the Blockchain.
When a user wants to withdraw funds from the channel, they send a transaction to the blockchain to settle the channel. This transaction will confirm all transactions made in the channel and distribute the remaining funds to each user.
What is State Channel?
State Channel is similar in nature to Payment Channel, however Payment Channel has a disadvantage which is the conversion of the general state of the Channel, so State Channel was created to solve this problem of Payment Channel.
State Channel acts as a layer between the blockchain and users. Once the channel is opened, each user will lock a certain amount of money into a smart contract on the blockchain. They can then carry out transactions between themselves without having to post those transactions to the blockchain. When a user wants to withdraw funds from the channel, they send a transaction to the blockchain to settle the channel. This transaction will confirm all status changes made in the channel and distribute the remaining funds to each user.
Comparison between State Channel and Payment Channel
|
Characteristic |
Payment Channel |
State Channel |
|---|---|---|
|
Purpose |
Allows users to make transactions at low cost and fast speed |
Allows participants to interact with each other and change the state of a Smart Contract. |
|
How it works |
Use a two-way ledger to record transactions |
Use smart contracts to record the state of interactions |
|
Application |
Payments, games |
Games, complex applications, and decentralized interactions |
The advantage of State Channel is that it can be used to perform more complex interactions, such as playing games or interacting with smart contracts, or can help reduce Blockchain congestion more effectively than Payment Channel.
State Channel’s Operating Mechanism
Overview of State Channel’s operating mechanism
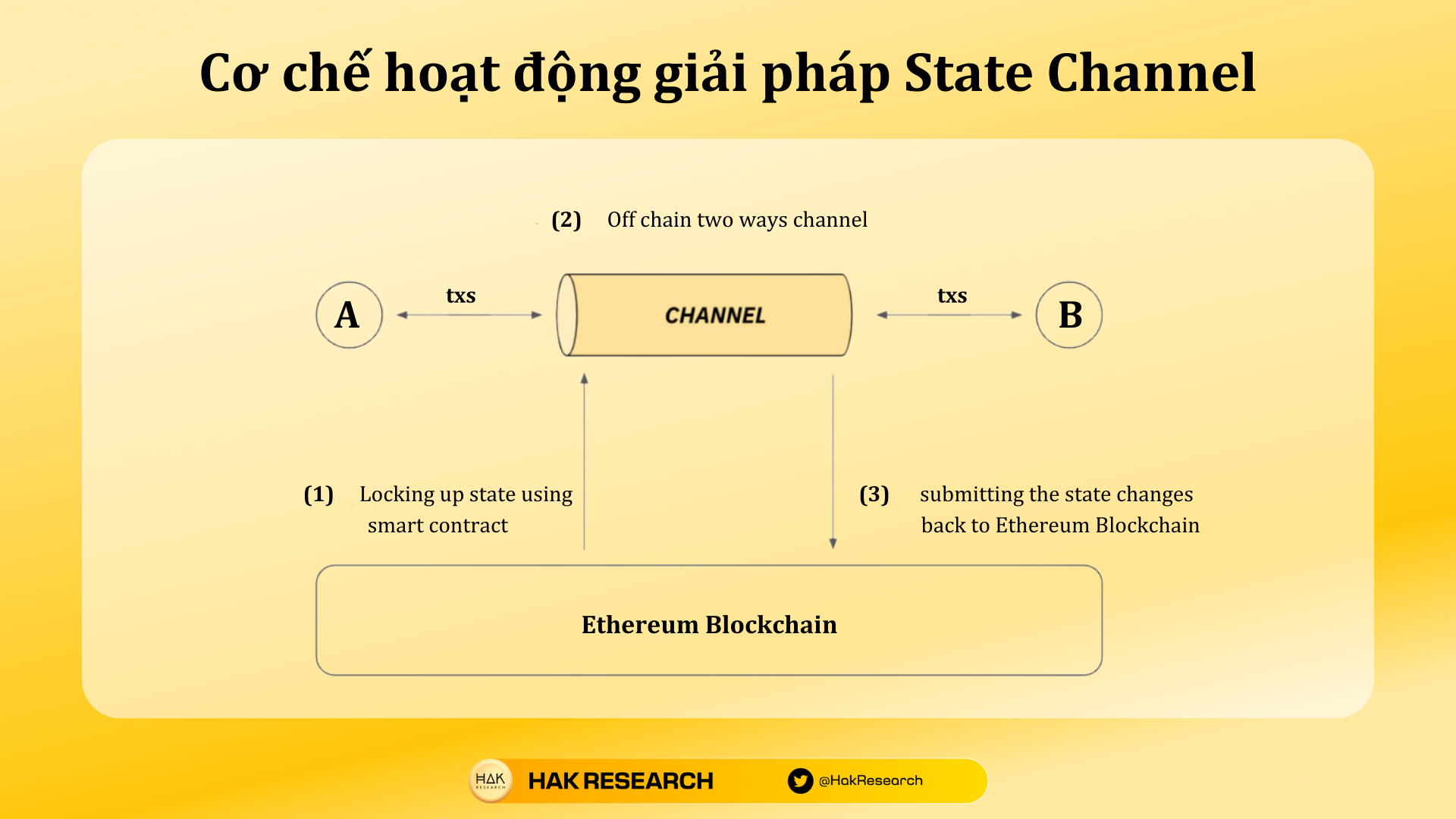
State Channel’s operating mechanism includes a number of activities as follows:
- Deposit money & open Channel
- Transaction and interaction in Channel
- Close Channel
- Resolve disputes that arise
Open Channel
Participating parties jointly initiate an on-chain smart contract, deposit funds into it, and must also sign the initial state of the channel. Participants can trade freely at near-instant speeds and with extremely low transaction fees. Until the channel is closed, then based on the final state, the participating parties receive their correct share.
Deposits into Channel are also considered collateral to avoid malicious behavior by participating parties. If the participating party commits malicious actions, it may be fined for part or all of the assets deposited into the Channel.
Use Channels
When the Channel is launched, participating parties will transact through signing transactions and sending transactions to each other for approval. The participating parties themselves must also sign to update the latest status of the Channel. Each transaction will include some information as follows:
- Nonce: similar to a transaction ID that is unique to mark the transaction. With nonce transactions considered fraudulent will be easily found.
- Old status of the channel.
- New channel status.
- Transaction content.
Close Channel
Closing the channel means the participating parties agree to send the agreed final state to the Smart Contract on Ethereum. If there are no problems based on the final balance on Channel’s latest status update, Smart Contract will redistribute the money proportionally to the participating parties. However, some problems will arise:
- The participants were offline and did not propose to switch network status.
- Participant carefully refuses valid status updates.
- The participant tries to give the old state to the Smart Contract.
- The participant proposes an invalid network state transition for others to sign.
When this event occurs, dispute resolution mode will be enabled and handled by Smart Contract.
Dispute resolution
In the context when one party is offline, the other party can send an On-chain Contract to close the channel and distribute money based on the latest status of the Channel. This factor helps participants to exit the Channel at any time and without the permission or appearance of the other party.
To exit the Channel, the user sends the Channel’s final state update to the On-chain Contract. If the final status update is signed by the participating parties, the funds will be redistributed to the two parties. However, if the other party’s sent status is deemed invalid, the other party can send a valid status update to the On-chain Contract. The State Channel is built so that the newer state will always outperform the old state.
This will activate the on-chain dispute resolution system where both parties will submit the status they think is valid and the On-chain Contract will arbitrate.
Interaction Between State Channel & Ethereum
Liveness – The ability to maintain
On-chain Contracts will be deployed on the underlying Blockchain to open the Channel and be responsible for that Channel itself. If the Contract is deployed on Ethereum, the Channel is always ready.
As for Sidechains, it will be much riskier because the Sidechain network is very vulnerable to attack and damage.
Security level
It can be said that Ethereum is one of the most secure and decentralized Blockchains today, so Channels operated by On-chain Contracts still inherit a certain level of decentralization and security. .
On-chain Contract’s use of Fraud Proof allows parties to transact safely and without risk even though there is no trust between the parties.
Finality – Finality
Once the On-chain Contract has confirmed that the final state is valid, the transaction will take place according to the final balance ratio on the state and this transaction will be irreversible. Even in a situation where one party tries to cheat but cannot provide evidence of the other party’s fraud, when the trial period expires, the money will still be sent in the most correct state.
State Channel Application
Fast & cheap payment
State Channel allows building a payment channel that is extremely fast and much cheaper than directly on-chain. Some of the advantages of using State Channel technology in payments include:
- Transaction Speed & Latency: Transaction speeds are almost instantaneous and much faster on Ethereum.
- Privacy: Transactions are not recorded on-chain, making it suitable for accounts that frequently interact with each other.
- Cost: Because transactions in the Channel do not require the participation of all main Validators, the transaction fee in the Channel is 0. There will only be fees for closing and opening the channel.
Low value transactions
Many businesses have to face many low-value payments, but if they use the services of third parties, the business will have to face a large cost, sometimes larger than the amount they need to pay. . That’s why State Channel is a solution.
Transactions in the Channel are free of charge and users only pay fees when opening or closing the Channel.
Decentralized application
There are many protocols that need a lot of interaction such as Gaming, NFT, ENS,… causing the protocol to have a headache on how to improve transaction fees. So what about some games for two people that are 100% on-chain but have no fees when transacting with each other and also do not need to trust each other to be able to transact.
Not only that, State Channel can also be expanded to many participants.
Besides strong advantages, State Channel has some disadvantages such as:
- Honest users for some reason do not store the final network state and cannot provide evidence of fraud. In this case, honest people can still lose money.
- If an honest user has had their Internet shut down for some reason, the cheating party can completely take over the money. Some solutions have been proposed but will increase the cost of using the State Channel.
- Putting money into a State Channel reduces users’ own liquidity on the Ethereum network because only by closing the channel can the money be recovered.
- On-chain dispute resolution can result in honest Users spending a lot of time, effort and money.
- Channel participants are often predetermined, so it will be difficult to expand in the long term.
Summary
State Channel is a Layer 2 solution suitable for payments with predetermined audiences. In some contexts State Channel is really useful but in the goal of Mass Adoption we need more than that. Hopefully through this article, everyone will understand more about what a Channel is? What is Payment Channel? What is State Channel?


