OLM is an extremely new and confusing term, first introduced by Andre Cronje and appearing recently due to the introduction of the project Bond Protocol. At its core, this term provides a solution to the problem of liquidity mining or Incentive of projects leading to Minting or releasing too many Tokens into the market over a period of time.
In this article, I will explain what OLM is? Pros and cons of OLM in the DeFi market.
You can refer to the articles about Options below to understand this article better:
- What is TapiocaDAO? TapiocaDAO Cryptocurrency Overview
- What is Bunni (LIT)? Bunni Cryptocurrency Overview
- What is twAML? Application Of twAML In DeFi Market
- What is Bond Protocol? Bond Protocol Cryptocurrency Overview
Problems encountered
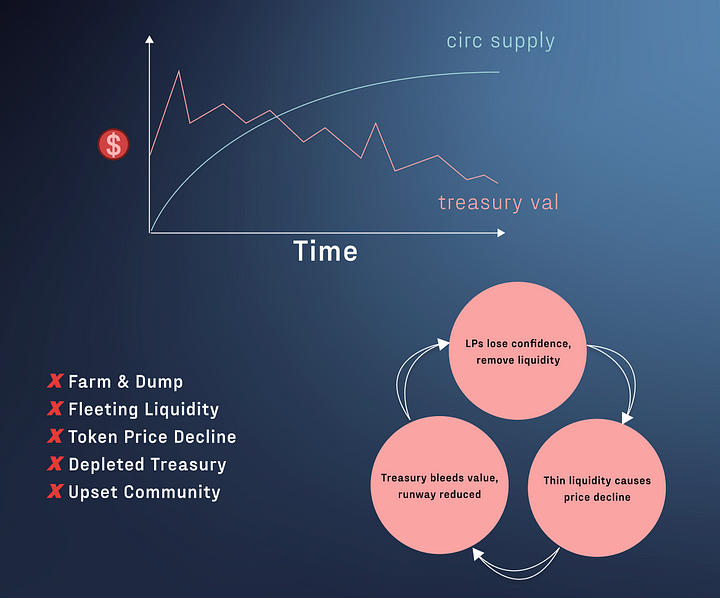
Traditional liquidity pool incentives (i.e. liquidity mining) have proven to be a double-edged sword. While effective for attracting initial liquidity, they lead to long-term inefficiencies and damage to cryptocurrency protocols.
Dependency on liquidity rented leading to the involvement of mercenaries (liquidity leasing), leading to a negative feedback loop: Liquidity floods in during the initial launch phase driven by high APY, only to dry up as token issuance Exhaustion notice.
As a result, after a while, the price of the Token as a reward will decrease. At that time, the profits are no longer attractive, so the supplier will leave the jobLiquidity was thin, slippage increased, sales were rapid, and token prices fell as participants rushed to exit.
What is OLM?
OLM stands for Options Liquidity Mining, which is the latest product of Bond Protocol inspired by the ideas of Andre Cronje, TapiocaDAO and Timeless Finance. OLM gives protocols the ability to mint and distribute ERC-20 call options called oTokens.
OLM is essentially a combination of liquidity mining, bonds and options. It brings efficiency to the liquidity mining program of the protocols. Helps the protocol attract liquidity, earn revenue while still providing benefits to liquidity providers.
Differentiating itself from other solutions on the market, OLM offers seamless integration with existing liquidity mining contracts, customizable oToken mechanisms, and static pricing. Options Liquidity Mining is a long-awaited solution to the problem of causing Token prices to reward strong Liquidity Mining and Incentive Dump.
Architecture
The OLM system is largely similar to the existing Bond Protocol architecture, including:
- Options Token (ERC20 Copy): Instance of an options token with specified parameters.
- Optional Teller: Handles tokenization, execution, withdrawal, and custody of payment tokens. Provide minting/redemption functions that allow other protocols to implement minting options that are not allowed
- Optional Liquidity Mining Contract: Implements liquidity mining that automatically generates option tokens and issues them as rewards.
OLM contracts are deployed from the Factory, allowing for quick, easy deployment of OLM instances. The issuer can manually adjust the strike price for each epoch or let it roll over each epoch (i.e. without oracle). For autonomous management, issuers with a reliable oracle can specify a discount from the price at the start of a new era.
Mechanism of Operation of OML
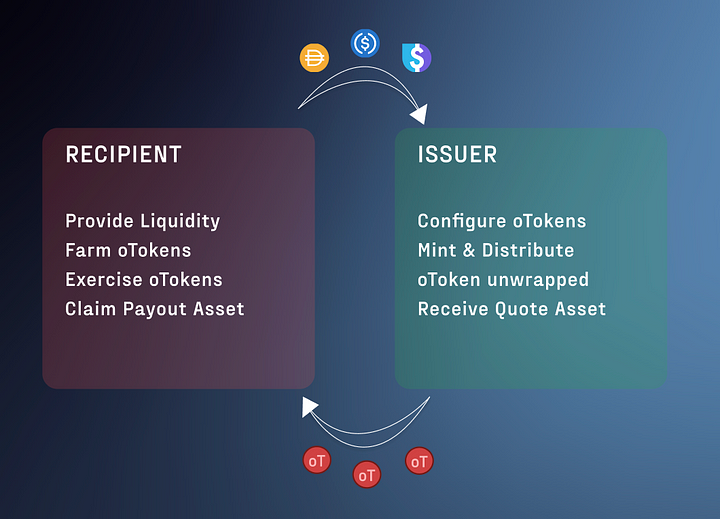
When it comes to the inner workings of OLM, the process is simple:
Fulfillment options: oTokens can be exercised during their eligibility and expiration dates, with a fixed exercise price determined upon issuance. In this case, the issuer recoups the strike price of the quoted asset required for exercise, while the buyer receives a back payment (strike price according to the option price).
Options that have expired or have not been exercised: In the event of expired or unexercised options, the issuer can reclaim the payment collateral initially provided to mint oTokens. This means the issuer no payment of liquidity incentive tokens. As a result, the benefits are shared between the issuer and the taker, while the downside is not exacerbated by subsequent farming/dumping operations.
The above process can be simply understood as the liquidity provider will receive oTokens with the parameters of liquidity commitment time, discount price and floor price. When providing liquidity, the liquidity provider is exercising the option to buy reward tokens for $0.
For example, let’s say a liquidity provider is providing some liquidity to protocol A and will receive 1000 oTokens at a 50% discount after 1 month of supply and with a floor price condition of $1. After the contract expires (also the liquidity commitment period), the provider receives 1000 governance tokens of protocol A, which are priced at $2. And the provider has the right to buy those 1000 Tokens for $1 and can then sell them for $2 to make a profit.
Another situation that occurs with the above example is that if when the contract expires, the price of the bonus Token drops to $1.8, then theoretically the supplier can buy at a 50% discount for $0.9. But the floor price is 1 dollar so you can still only buy at 1 dollar. If the provider does not want to exercise this right, they can cancel and this amount of reward Tokens will be transferred to the DAO.
Through the above example, we can see that the protocol will have an additional amount of permanent assets by selling Tokens at a discount price. Because there is a floor price, it is possible to support the price of the Token as well as through option contracts to help negotiate capital commitment time.
This is a typical example of OLM, but for many other OLM projects they may have different mechanisms or conditions such as not applying floor prices, applying general discounts like Bunni or flexible discounts like TapiocaDAO,…
Advantages and Disadvantages of OLM
Advantage
- Increase revenue for the protocol.
- Reduced risk of protocol token dumping.
- Liquidity is committed within the specified time.
- Guaranteed profits for liquidity providers.
Defect
- The process is somewhat more complicated than usual Liquidity Mining.
- Lock up liquidity provider capital.
- The supplier must continue to spend some more capital to buy Tokens at a discount and sell them for a profit.
- The token price drops too much when the contract expires and the provider risks not making any profit from providing liquidity to the protocol.
Personal Projection
From combining the Liquidity Mining, Bond and Option models, OLM was born to solve a major problem existing in the market. OLM is truly a great solution to help limit the liquidity rental and farming/dumping problems that occur every day in the DeFi market.
The first is KEEP3R developed by Andre Cronje which has proven effective and attractive in providing liquidity. Although this project is lacking growth momentum amid difficult market times. But from this idea pushed the birth of later protocols such as Bond Protocol, TapiocaDAO, and Bunni of Timeless Finance.
Maybe the upcoming market will use this model a lot and it becomes the standard for projects using the Liquidity Mining model.
Summary
So I have clarified what OLM is? Pros and cons of OLM in the DeFi market. Hope this article brings you a lot of useful knowledge!


