Nomad, a cross-chain bridge, has raised 22 million USD in Seed Round from large funds such as Polychain Capital, 1kx, Ethereal, Hack VC, Circle, …
Nomad allows token transfer between ecosystems and between different Blockchains. Nomad’s goal is to create links for users and developers to interact safe in on blockchains.
In August 2022 Nomad is attacked and had $190 million taken away from the bridge (according to data from DefiLlama).

So what is Nomad? How does it work? Let’s find out with Weakhand in this article!
To understand more about Nomad, you can read the following articles on Hakresearch Website:
- What is Celer Network (CELR)? Celer Network Cryptocurrency Overview
- Working Mechanism of LayerZero, a New Generation Multi-Chain Bridge
- What is Wormhole? Wormhole Cryptocurrency Overview
- Bridges: Design, Trade-offs, and Opportunities
What is Nomad?
Nomad is a cross-chain bridge (Cross-chain messaging) allows transferring tokens back and forth between ecosystems and between different Blockchains such as Avalanche (AVAX), Ethereum (ETH), Evmos (EVMOS), Milkomeda C1 and Moonbeam (GLMR).
Because it connects very few Chains and supports few Token types, Nomad is struggling to keep up with its competitors such as: Wormhole, LayerZero, Multichain, Celer,…
Nomad has interoperability to send arbitrary messages between blockchains, allows applications to transmit data to each other across different blockchains through a message sending and receiving system.
Nomad uses a validation mechanism with Optimistic proof, meaning that for a period of time if no validator objects, the data is defaulted to true. That makes Nomad work slowly. Although in theory security is still guaranteed, Nomad is still attacked by Hackers. And until now, the project has not been able to retrieve the previous user files.
Application:
- Users can connect tokens between chains.
- Asset issuers can deploy tokens on chains.
- DAOs can facilitate the implementation of cross-chain governance proposals.
- Developers can build native cross-chain applications (xApps).
Nomad’s Operating Model
Because it uses Optimistic proof, the authentication process that takes place on Nomad takes a lot of waiting time. People who participate in data validation are called Watchers. In theory, just one honest verifier could prevent false data.
Process for transferring messages on Nomad:
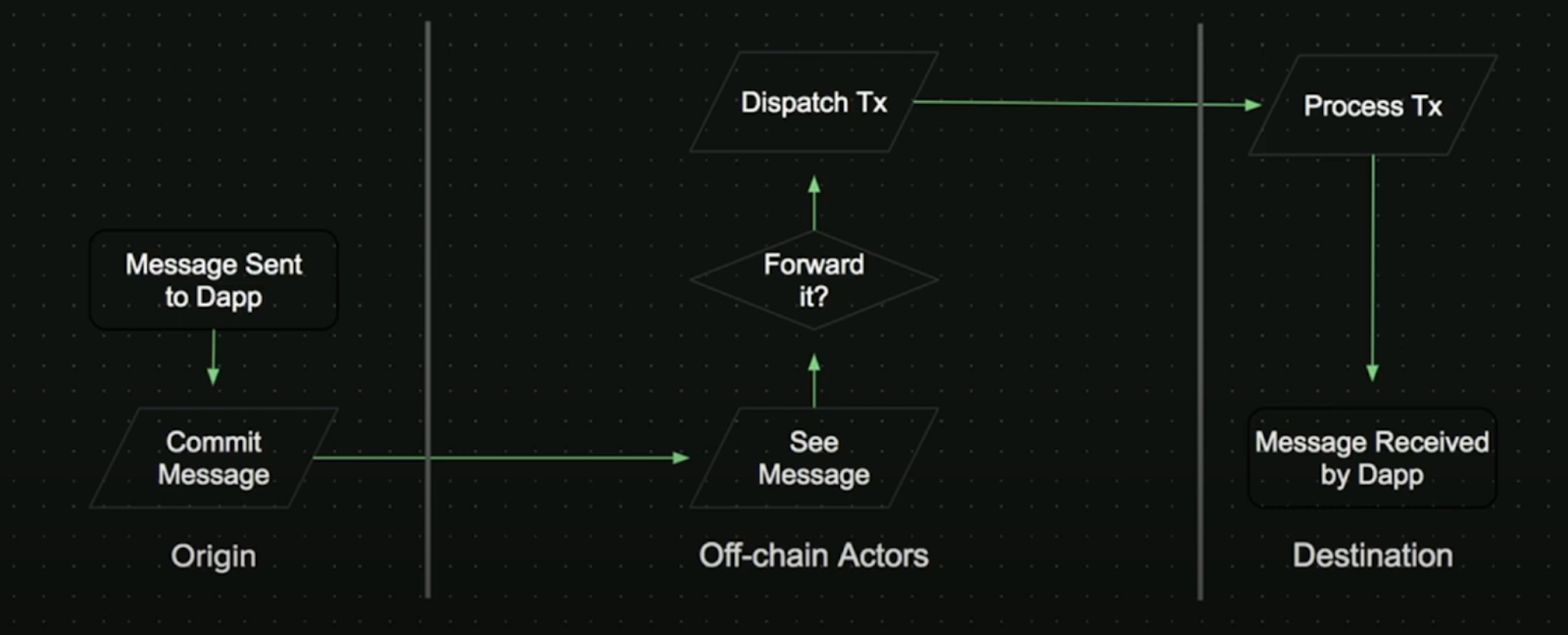
- The DApp transfers messages from users to Commit Message. Commit Message is the part of Nomad that is mounted on the networks.
- Commit forwards the message to See Message. Here, the Watchers will check whether the message is true or not. If it is correct, the network will default to the correct and authenticated data after the timeout. If someone discovers a mistake, report it to the system, then the order will be canceled.
- Once the message is acknowledged, the message is passed to Process Tx. This is also a part of the Nomad that is attached to the target chain.
- Finally, Process will pass the message to the dApp for execution.
Nomad supports asset transfers through a message passing mechanism that impacts asset pools. This mechanism is similar to LayerZero’s asset transfer mechanism. But the difference between Nomad and LayerZero is the authentication mechanism as well as the way the message is transmitted.
Development Roadmap
Update…
Core Team
Update…
Investor

The project successfully raised capital of 22 million USD in Seed Round from large funds Polychain Capital, 1kx, Ethereal, Hack VC, Circle, … with a valuation of 225 million USD.
Partner
The project is working closely with Connext Network
Tokenomics
The project does not have a Token yet
Project Information Channel
- Website: https://nomad.xyz/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/nomadxyz_
- Discord:
Summary
Nomad is a cross-chain bridge (Cross-chain messaging), considered a safe, secure, cheap, and easy-to-deploy bridge.
Nomad has very wide application potential. Nomad can be viewed as an infrastructure for building Cross-chain applications such as: Cross-chain AMM, Cross-chain Lending, NFT bridge, Wallet,…
But in August 2022 Nomad was attacked and suffered $190 million in damage on the bridge. This is the 4th largest Hack in crypto history to date. The attack occurred due to a smart contract security vulnerability. This was stated in a security audit report conducted by Quantstamp.
Up to now, our team has stopped at investigating hackers, posting messages to reclaim hacked assets and fixing security errors. However, the Hackers have no intention of returning assets to Nomad.
Hope this article provides everyone with a lot of useful information!


