Royalty fees are always a topic of discussion in the NFT user community. Some people think it’s necessary to honor the creator, but others don’t because it creates a big barrier for users to participate in NFTs. So what exactly is the Royalty Fee? Let’s join the Weakhand team. Find out in this article.
What Is NFT Royalty Fee?
NFT royalty fees are payments paid to creators each time their work is sold on the secondary market. Royalty fees can vary depending on each NFT collection, but a rate of 5-10% of the sale price is generally considered standard. For larger NFT collections, lower royalty fees of around 2.5% are common.
For example: An NFT collection has a 10% royalty fee on OpenSea and currently the floor price for the collection is 20 ETH. A user wants to sell 1 NFT from a collection at a floor price on the OpenSea marketplace. In addition to transaction fees, he must pay a royalty fee of: 20 * 10% = 2 ETH for each sale of his NFT.
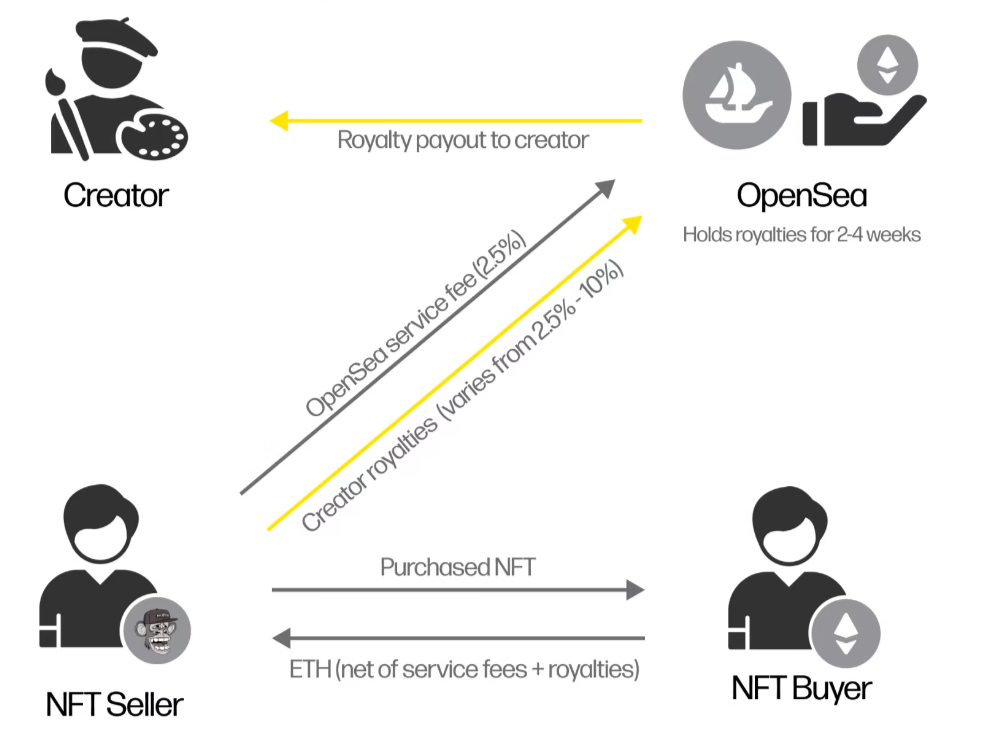
What is a copyright fee?
This solution allows NFT creators, artists and brands to generate an ongoing revenue stream from their NFT collections, which they can then use to grow their products and has the potential to provide utility as well as additional value to NFT holders.
However, not all projects apply copyright fees to their NFT collections. Degods and Moonbirds are two typical collections in eliminating copyright fees. Some other popular projects that are still applying copyright fees include:
- Azuki: 5% fee on secondary sales distributed to Chiru Labs.
- Doodles: 5% royalty fee, half of which goes to the community treasury (Doodlebank).
- Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC): 2.5% secondary sales fee distributed to Yuga Labs.
- Meebits: 5% of royalties distributed to Yuga Labs.
Just multiply the trading volume of the collections by their royalty fees, and it’s not hard to see that the licensing fees have created a huge revenue stream for the creator, the web3 entertainment company. According to data from Nansen in July 2022, Yuga Labs – the company behind 4 famous collections earned $148M USD in licensing fees.
How Do NFT Royalties Work?
Royalties operate through Smart Contracts which are automatically executed agreements. Therefore, when the terms and conditions are met they will be enforced on secondary trading markets such as OpenSea, Blur, LookRare,…
Once a piece of digital art is created, the NFT artist can set up a Smart Contract with royalty agreements according to their wishes (usually from 2 – 10% of the sale price). When the NFT is sold, the Smart Contract is automatically executed and sends the royalty amount to the creator’s predetermined wallet address. Royalty fees are often paid in cryptocurrency such as: ETH, SOL, etc.
In addition, the Ethereum community also recently introduced a new standard for programmable copyright fees called ERC 721C, an extension of ERC 721 to provide NFT creators with control and customization. Higher adjustments to royalty fees in NFT collections.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Royalty Fees
Advantage
The following are the advantages that copyright fees bring:
- Ongoing revenue for creators: Royalties provide artists with an ongoing revenue stream. This serves as recognition for their original work and encourages artists to continue producing high-quality content.
- Allocation of value to parties: The royalty system helps distribute value more equitably in the NFT ecosystem. This is achieved through Creators, Collectors and Traders all profiting from the NFT trading process.
- Community building: The owner and creator of the NFT is part of the collection. So when a project has an active community it invisibly increases the value of the NFT. This is beneficial for both NFT owners and project creators.
Defect
Disadvantages of copyright fees are:
- Royalty terms are unclear: Royalty terms may vary across NFT Marketplaces. For example, Superare – a luxury digital art marketplace charges a 10% royalty fee on each transaction. However, X2Y2 and Magic Eden chose to pay the optional license fee. The lack of consistency across platforms makes it difficult for both creators and users to gain access.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts can have some vulnerabilities such as integer arithmetic that can lead to disputes or incorrect distribution of royalties.
- Price Manipulation & Wash Trade: Some whales may manipulate and inflate the value of NFTs, affecting royalty revenue from the project.
- Reduced liquidity: Having to pay a large royalty fee after each transaction could impact user demand for NFTs.
Why NFT Marketplaces Eliminate Royalty Fees
As mentioned above, some NFT Marketplace platforms may view royalty fees as a direct competitor to their revenue stream. If an NFT collection imposes a flat royalty fee of 5% and the NFT Marketplace platform charges 2.5% per transaction, the total fee paid by users is 7.5%, which can be considered a barrier huge for users.
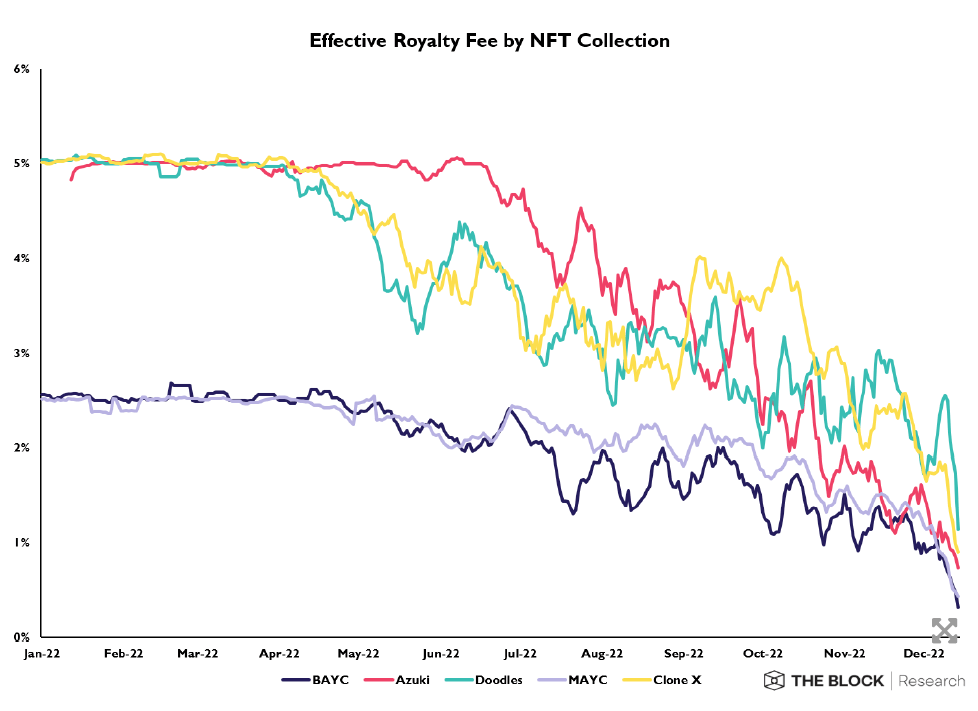
Statistics on copyright fees of popular NFT collections
Therefore, the trend of reducing royalty fees appeared in the summer of 2022. SudoSwap – the first platform to do this raised the opinion that royalty fees are “ineffective” because buyers often need to see the asset Their prices increase by at least 10% just to break even on secondary sales.
Instead, Sudoswap applies a 0.5% fee to all transactions and bypasses any royalty agreements. Some believe this could help create a healthier trading economy, while others feel NFT creators will need to receive a portion of the profits if their collections are to achieve success. labour.
Other NFT Marketplace platforms like LookRare, Magic Eden, and X2Y2 have all eliminated the NFT licensing fee model. Their new royalty options system allows NFT buyers to decide to honor the artist’s royalty policy when making a purchase.
summary
The incentive for NFT Marketplace platforms to reduce royalty fees is simple because it attracts more users to join the platform. But this faced many mixed opinions from the creators. Regardless, the royalty fee is still part of the NFT ecosystem and it will be adjusted appropriately to suit the community’s wishes. Above is all the information I want to introduce about copyright fees, hope everyone has received interesting knowledge.


