Centralized liquidity is showing effectiveness and widespread application on Dexes. But most Dex AMMs reuse the model of Uniswap V3. This is too boring, Trader Joe also proved to the market its creativity when introducing the centralized liquidity model Liquidity Book.
What is Liquidity Book? Liquidity Book is also another version of the centralized liquidity model in AMM Dex. However, this model is different and new as well as has its own advantages compared to Uniswap V3.
So what is Liquidity Book? What are its advantages and disadvantages as well as its effectiveness? Let’s find out in this article! To understand more about the Liquidity Book model, you can read the articles below:
- What is Centralized Liquidity (CLMM)? Outstanding Projects In The CLMM Array
- What is Maverick Protocol (MAV)? Overview of Cryptocurrency Maverick Protocol
- What is Uniswap V3? Is Centralized Liquidity Changing the Crypto Market
- Uniswap & Trader Joe: Centralized Liquidity War. Is Joe the Winner?
What is Liquidity Book?
Liquidity Book means “liquidity book”, which is another version of the centralized liquidity model (CLMM). This model was first introduced by Trader Joe at the end of 2022. This is an innovation and has a few differences compared to the Uniswap V3 model.
Liquidity Book allows providers to liquidate within a price range, which will include one or more small price zones called Bins. The liquidity pool uses a constant sum formula, uses dynamic transaction fees, and introduces the Bin concept.
The Liquidity Book model provides traders with an extremely good price with zero slippage, the price also does not move when trading within the range of 1 Bin. Helps liquidity providers use capital effectively.
Mechanism of Action
Bin
Bin is often referred to in Vietnamese as “Bin”, Bin is the smallest price range pre-installed by the Pool creator. Liquidity adders can choose to provide liquidity in one Bin or multiple Bins. Different from Uniswap V3, the liquidity provider in a price range that is capped at both ends is called a “Tick”.
The liquidity book allows liquidity to be distributed across separate buckets with a fixed width. Liquidity can be exchanged at a fixed price per barrel. Each bin represents a single price point, and the difference between two consecutive bins is the bin step.
Liquidity Pool
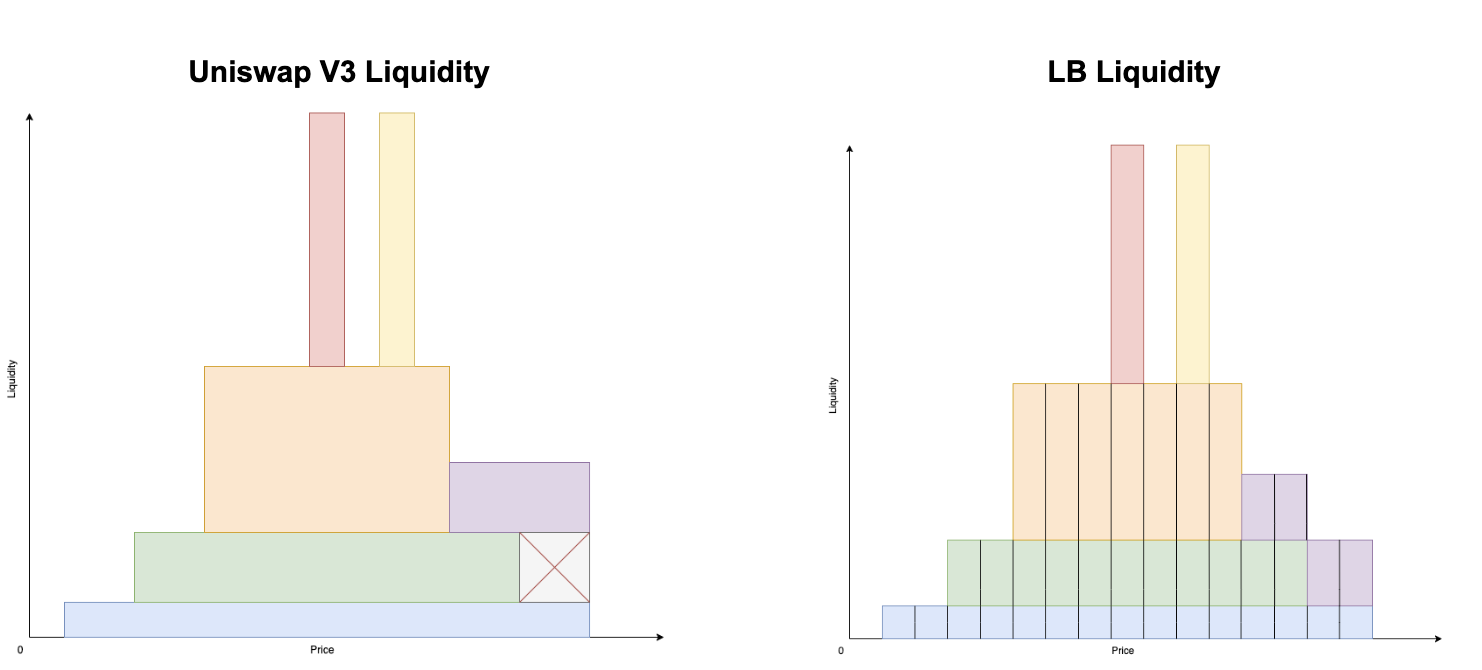
The way Liquidity Book aggregates liquidity is somewhat different from Uniswap V3. In Liquidity Book, liquidity is aggregated vertically across each bucket, and in Uniswap V3, liquidity is aggregated horizontally. The main benefit of vertical aggregation is that it allows for possible liquidity replaceable and flexible to implement programs such as liquidity management, Farming,…
User liquidity positions are encoded as Tokens according to the LBToken standard, which is LB’s own Token standard. LBToken tracks the amount of liquidity added to each bucket for each user in a given pair. For all in-depth purposes, it is almost the same as an ERC 1155 token, but without the functions and variables associated with NFTs.
The total formula remains unchanged
Centralized liquidity AMM pools are often used formula x * y= kbut Liquidity Book uses it formula x + y= k (total remains unchanged). This formula shows that you will not experience price slippage when the liquidity transaction is in 1 Bin. If so, how does the price move? Liquidity Book will move to a new price or a new Bin if the current trading Bin runs out of liquidity. (This will be explained more clearly in the “mechanism of action” section below).
Dynamic fees
The liquidity book applies dynamic fees to cover losses for LPs during times of high market volatility. Traders pay swap fees to liquidity providers when making swaps. Total swap fee There will be two components: facility fee (fb) and a variable costs (fv), is a function of the instantaneous price movement. The fee rate will be applied to the swap amount in each liquidity compartment and distributed proportionally to the liquidity providers in that compartment.
- In V2.0, fees will be separate from liquidity and can be requested by liquidity providers.
- In V2.1, fees are added to existing positions and held in reserve. Liquidity providers can request them when withdrawing funds from the liquidity pool.
The base fee of a market is configured by the protocol owner (DAO) and determined by base coefficient (b) and step bin (S): fb =b * S (Similar to fee calculation on other DEXs).
On the other hand, variable fees depend on market fluctuations. It will be affected by swap frequency, doing large swaps across multiple barrels (based on large price movements) will also increase it. Fees are calculated and distributed per box.
Liquidity Book’s operating mechanism
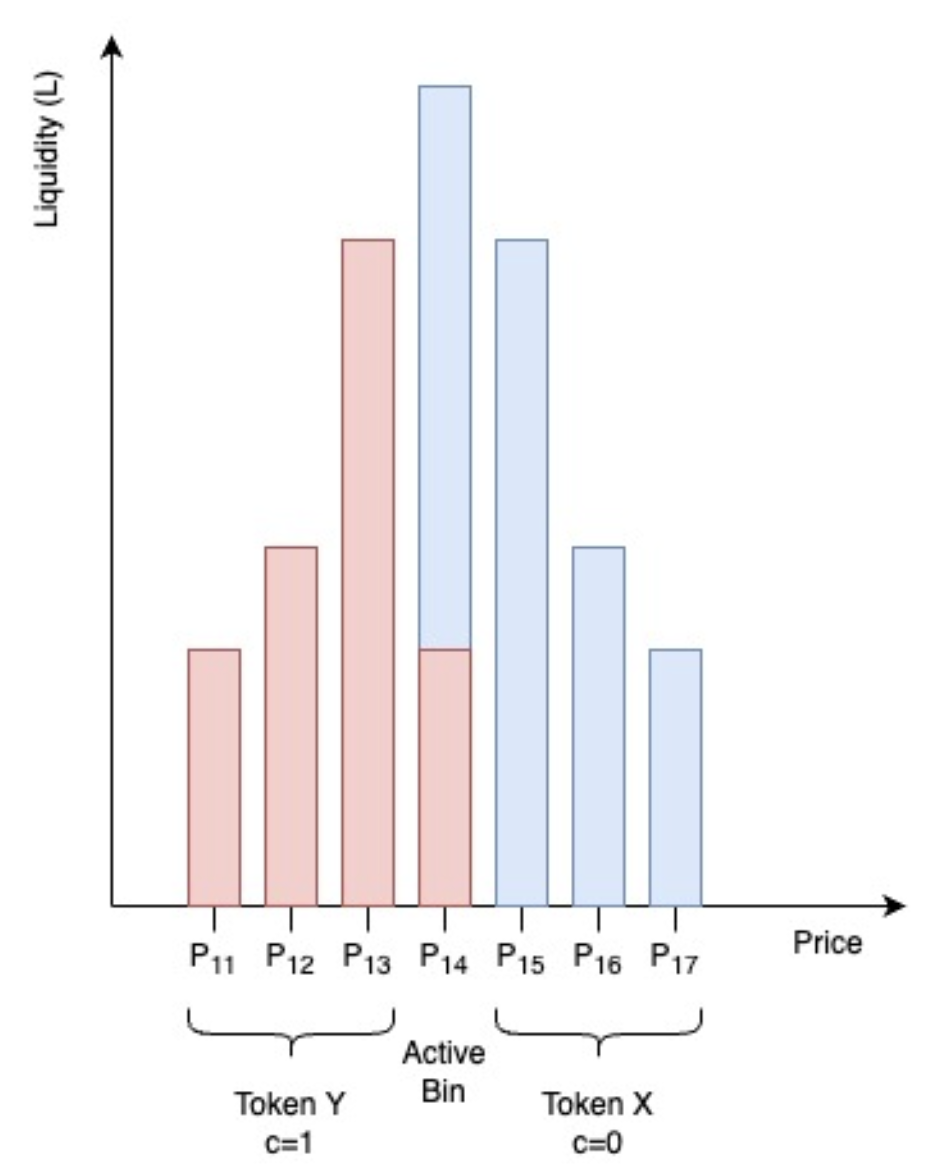
To have trading liquidity, the provider needs to provide liquidity into a Bin or a Bin area. Suppose the provider is providing liquidity from Bin 11 to Bin 17, each Bin will have a different price (for example the Bin step is 0.1$ and the price of the current active Bin (Bin 14) is 10$ then : Bin 11 is $9.7, Bin 12 is $9.8, Bin 13 is $9.9, Bin 15 is $10.1, Bin 16 is $10.2, Bin 17 is $10.3.
When a trader makes a Swap at the current price, which is $10 in (Bin 14), all transactions in Bin 14 are calculated at the price of $10 (in Bin 14, the red part is Token Y and the green part is Token X and the Token pair will be paired as X/Y). If traders buy all Token In the opposite case, if traders sell too much Token That’s how Liquidity Book works.
Usually there is only one active Bin in the Liquidity Book, that Bin also represents the current trading price of the asset and this Bin is receiving transaction fees. However, there are some cases where large trading orders or many orders are executed at the same time and the liquidity of 1 Bin cannot be met, leading to the use of many Bins at the same time, and prices also slide across many Bins. At this time, the transaction fee also increases to compensate for the loss to the liquidity provider and the transaction fee of that order is divided among the Bins used.
Highlights of Liquidity Book
- No price slippage: Traders can swap tokens without slippage in the bins (Bins).
- Pricing surge: Liquidity providers earn additional dynamic fees during times of high market volatility.
- High capital efficiency: The liquidity book can support high volume trading with low liquidity requirements, i.e. very high capital utilization and liquidity efficiency.
- Flexible liquidity: Liquidity providers can build flexible liquidity distribution according to their strategy.
Application
With properties such as centralized liquidity and non-slippage transactions, Trader’s Liquidity Book is very useful for asset pairs at par, assets with large capitalization and in a stable market environment with very little fluctuation. As for the volatile environment, both Liquidity Book and Concentrated Liquidity liquidity models have limitations. Liquidity Book is more limited because of its slow price response. But when the market stabilizes, Liquidity Book shows superiority over Concentrated Liquidity.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantage
- Transactions are not subject to price slippage.
- Effective use of liquidity, even a low amount of liquidity can accommodate a large amount of transactions.
- Dynamic fees help reduce losses for liquidity providers.
- Using LPToken to represent a liquidity position provides more flexibility.
- Dividing liquidity into small Bins also makes liquidity aggregation easier.
Defect
- Usually price reaction is slower than the market.
- Liquidity providers suffer larger losses.
Compare Liquidity Book With Concentrated Liquidity
|
|
Liquidity Book |
Concentrated Liquidity |
|---|---|---|
|
Model |
Centralized liquidity |
Centralized liquidity |
|
Liquidity supply zone |
One or more Bins |
Area limited by Tick |
|
Recipe |
Constant sum (x+y=k) |
Constant product (x*y=k) |
|
Minimum liquidity split |
Bin (is a basic point or a region of many basic points) |
Basic point |
|
Aggregate liquidity |
Vertically aggregated |
Aggregate horizontally |
|
Liquid position |
Fungible (Token) |
Non-fungible (NFT) |
|
Liquidity distribution |
Can follow any shape |
Evenly on the base points |
|
Transaction fees |
Basic fixed fees and dynamic fees |
Basic flat fee |
|
Inflation |
None or low |
Low or high |
|
Liquidity efficiency |
High |
Short |
Personal Projection
Trader Joe’s Liquidity Book model is one of the quite innovative centralized liquidity models and has its own advantages and disadvantages compared to the Uniswap V3 model. The Liquidity Book model also proves its appeal as an AMM Dex with trading volume in the Top 5 markets.
Every emerging technology has its own pros and cons. While Liquidity Book solves the slippage problem for traders, it puts liquidity providers at risk of more losses. And to solve this problem, Liquidity Book applies a dynamic fee in addition to the basic fee so that when the market fluctuates, LP’s losses are compensated by this fee.
So it could be that the Liquidity Book model is a piece of the puzzle, a project that supports the problems or weaknesses of Uniswap v3 or other Dexes.
Summary
Liquidity Book is one of the innovative centralized liquidity models started by Trader Joe. It brings efficiencies in its own niche and along with that also comes weaknesses.
So I have clarified what Liquidity Book is? Advantages and disadvantages of the Liquidity Book model. Hope this article brings you a lot of useful information and knowledge!


