We are very familiar with Layer 1 and Layer 2 projects, so what is Layer 3? What effect does it have in the blockchain world?
Bitcoin’s overall market capitalization is over $1 trillion as of April 2021. Ethereum is growing with the continued rise of the DeFi ecosystem, ensuring a favorable platform for decentralized applications central. The continuously expanding demand for multilayer blockchains has created favorable implications for the capabilities of Layer 3 protocols in the blockchain ecosystem.
What are these Layer 3 solutions in the world of blockchain? How does it contribute value to the overall blockchain ecosystem? You can learn about the advantages of Layer 3 blockchain protocols and its detailed examples in the article below!
Why does Blockchain need Layer 3?
The obvious question on everyone’s mind regarding Layer 3 solutions in blockchain would refer to the need for Layer 3. Any individual familiar with blockchain must have heard of blockchain trilemma. This definition separates three important elements in a blockchain network. Interestingly, the origin of blockchain layers begins with trilemma, which implies that blockchain networks can only satisfy two of the three properties.
The Blockchain Trilemma
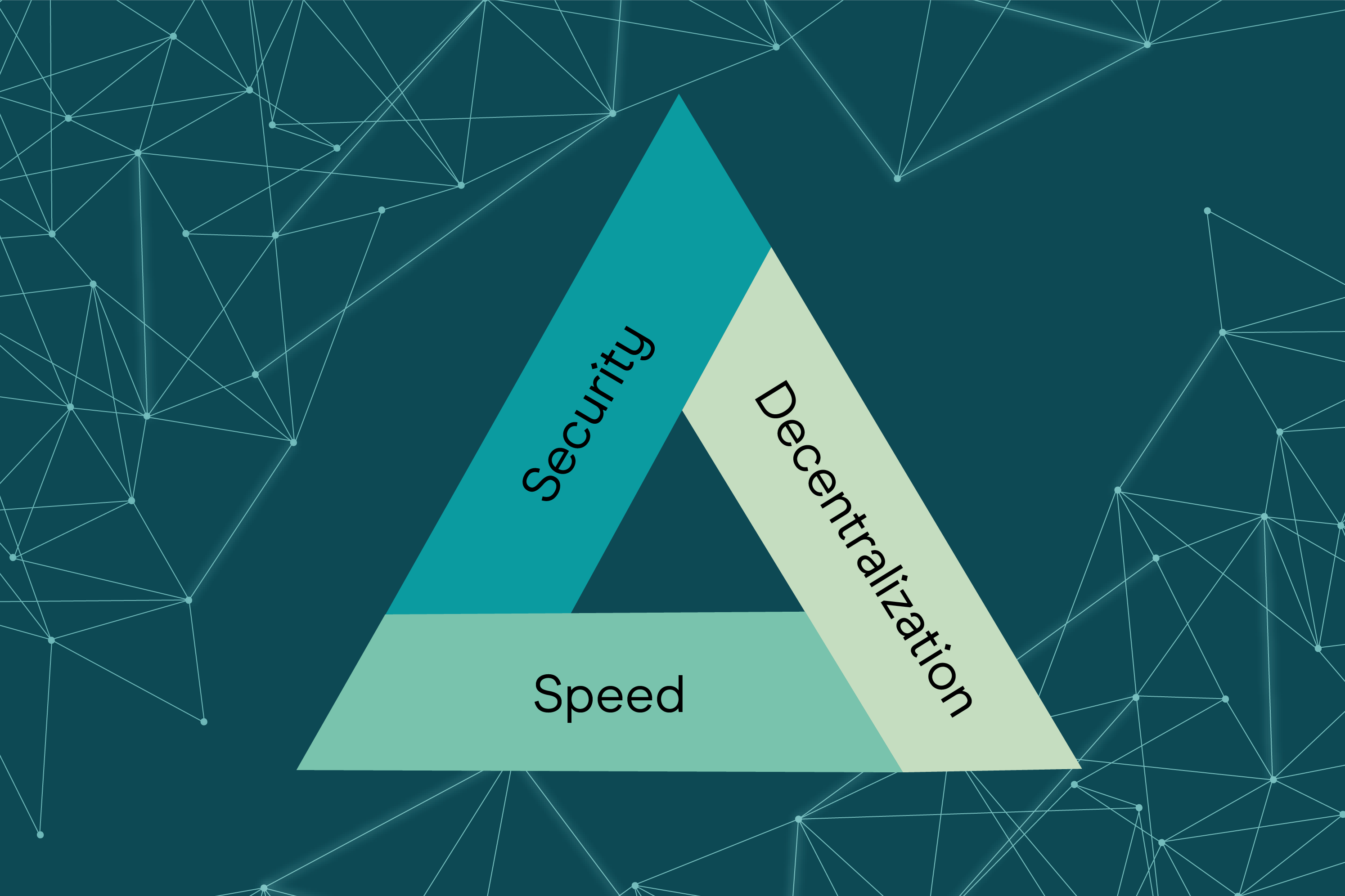
Three elements in Blockchain Trilemma include decentralization, security and stability. Almost every blockchain project has to sacrifice one of the factors to achieve better performance with the other two. You can find trade-offs in popular examples like Ethereum and Solana.
Ethereum and Bitcoin focus more on security and decentralization, while Solana focuses more on stability and security. The scalability trilemma presents a serious problem for integrating the three elements in a Layer 1 blockchain. Therefore, a multi-layer structure can provide an efficient and cost-effective solution regulated effectively tailored to achieve scalability, security, and decentralization.
Now, it’s important to ask yourself whether a Layer 3 type of protocol is necessary when you can have Layer 2 protocols.
Blockchain Interoperability
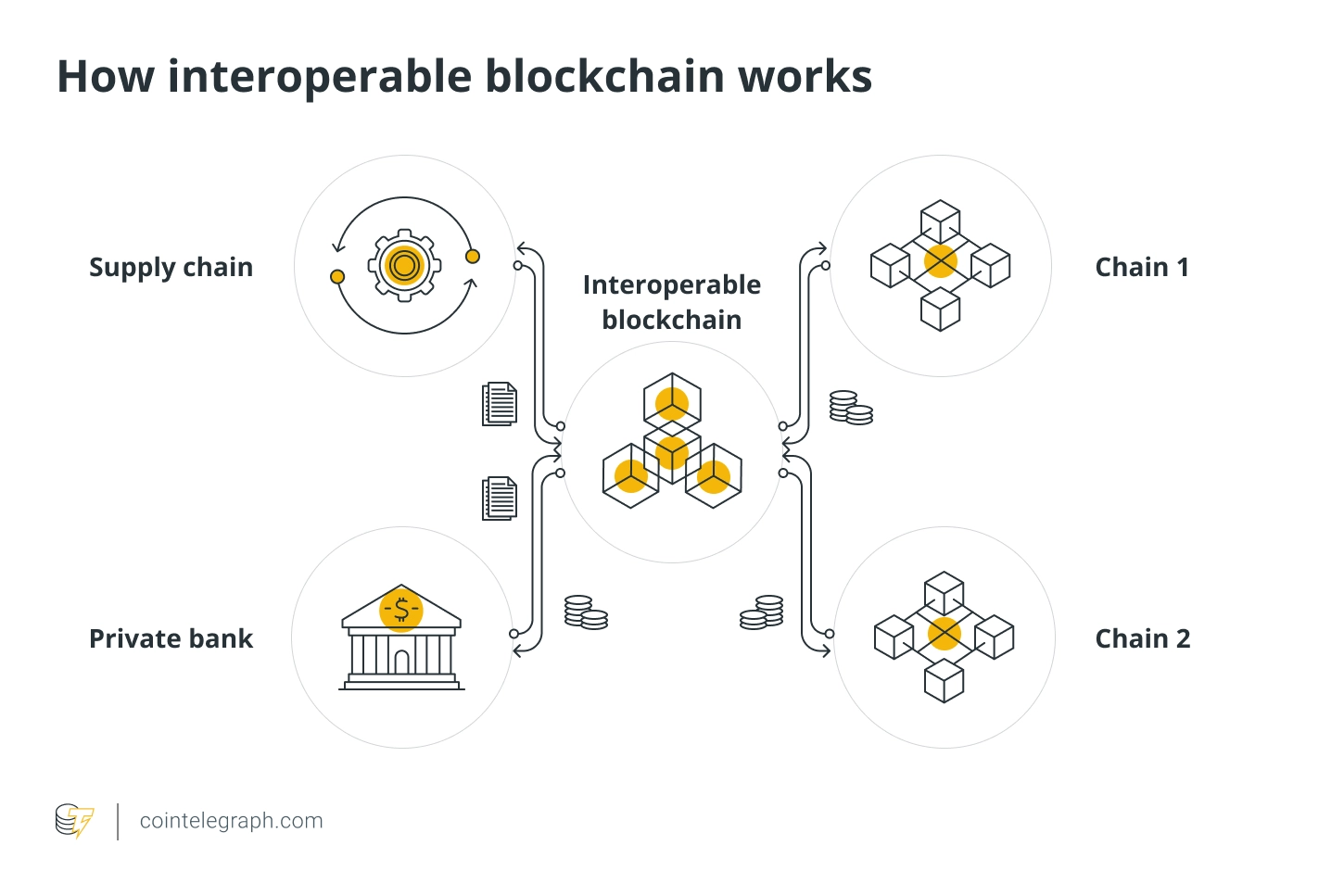
The fundamental reasons for introducing multi-level architecture in blockchain networks show the perfect solution to scalability problems. Layer 2 blockchain solutions can help solve problems related to scalability. So what is the demand for Layer 3 blockchain projects? In fact, Blockchain Trilemma is not the only fundamental problem affecting cryptocurrency market participants. On top of that, Layer 2 solutions do not address interoperability concerns. The Layer 2 protocol does not provide anything to view, access and exchange information between different computer systems.
The definition of interoperability in the blockchain space is also known as cross-chain functionality. It implies that two different blockchain networks with their own ecosystems can communicate with each other and participate in transactions without the need for a centralized intermediary. For example, it is practically impossible to transfer Bitcoin to the Ethereum blockchain and use Bitcoin on many DeFi applications. Almost all solutions that provide flexibility for crypto trading across multiple dApps and DeFi solutions have some form of centralized control.
The need for Layer 3 blockchain protocols becomes prominent when you think of popular DeFi applications. Lending protocol, Aave, and decentralized exchange, Serum, are operating on different blockchain networks. Therefore, practically no one can access the services on these platforms. So, the lack of interoperability between blockchain networks is the most important reason to introduce Layer 3 solutions.
So What Is Layer 3 In Blockchain?

Layer 3 protocols are essentially unique solutions to empower different blockchain networks with cross-chain capabilities. The main goal of Layer 3 solutions will focus on achieving real interoperability without relying on middlemen or custodians. One of the interesting highlights of Layer 3 solutions refers to the emphasis on similarity to the layered structure of the internet.
Just like Layer 1 blockchains, Layer 2 protocols have distinct characteristics that distinguish them from each other. Services on the Layer 2 protocol are often associated with specific blockchain networks. For example, the Lightning Network has been designed specifically for Bitcoin, while the Optimism protocol works for Ethereum.
How does Layer 3 solve interoperability problems?
The interplay between Layer 2 and Layer 1 solutions creates the need for implementing interoperability protocols on a different third layer. If you search for the answer to “What is Layer 3 in blockchain?” You will find notices of many differences between Layer 2 and Layer 1 blockchains. Layer 3 aims to solve the problem of interoperability while ensuring process simplicity in the Layers below. .
Layer 3 works on the abstraction of different elements such as technology, functions and features to serve users in different ecosystems. The abstraction of such differences through Layer 3 or L3 protocols helps different networks and ecosystems to communicate, connect and interact with each other.
An overview of every type of Layer 3 protocol will show how they work to solve interoperability problems. They work in a similar way to internet protocols and ensure data transmission in packets. The advantages of Layer 3 solutions also focus on quantifying value in packets along with routing value packets across multiple DLT networks. Layer 3 protocols can then ensure efficient connectivity between Layer 1 and Layer 2 chains, along with associated applications and services.
Layer 3 Protocol Examples
The most important part in discussing Layer 3 solutions is obviously showing detailed examples. Many new Layer 3 projects have been launching interoperable protocols to facilitate connectivity between different blockchain networks and Layer 2 services or protocols. Below is an outline of some examples. Top examples of Layer 3 blockchain projects you should consider.
Interledger Protocol
Ripple’s Interledger Protocol or ILP is actually the most popular Layer 3 solution on the market today. Ripple has a multi-layered architecture with three distinct layers serving distinct functions. Layer 1 acts as the blockchain ledger, while Layer 2 has local area networks or LANs.
On top of that, the Layer 3 protocol in Ripple, Interledger Protocol, aims to provide faster and cost-effective transactions on the Ripple blockchain. As one of the most well-known Layer 3 blockchain protocols, Ripple’s Interledger Protocol provides an effective roadmap for implementing interoperability within the blockchain ecosystem. You may notice how ILP works like IP or Internet Protocol works.
IBC Protocol
The IBC Protocol or Cosmos Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol is another interesting example of the use of blockchain layers in the architecture of projects. A closer look at Cosmos’s architecture reveals that it also has a three-layer architecture.
Tendermint Core serves as a Layer 1 protocol, while Cosmos-SDK supports Layer 2 protocol functions. The IBC protocol can help any application with reliable and inter-module communication. safe. On top of that, you can also identify the benefits of multi-chain smart contracts along with cross-chain asset transfers with the IBC protocol.
As one of the leading Layer 3 protocols, IBC facilitates a reliable and secure module for connection between blockchain networks. It supports various tasks, including data transfer, authentication, and transactions across multiple blockchain networks.
ICON
ICON is one of the only examples of a Layer 3 protocol type that operates as a standalone solution. ICON’s biggest highlight is its Layer 3 protocol that points to its partnership with the Seoul government and Samsung. The interoperability protocol works by collecting all blockchain data on one layer to connect multiple blockchain networks. ICON presents a reliable solution to introduce a single unified set of multiple blockchain networks.
Quant
The next most popular example among Layer 3 blockchain protocols is Quant. Developed as a trusted solution for enterprise blockchain networks, Quant helps connect public and private chains. Quant leverages Overledger’s DLT gateway along with a variety of unique solutions to support interoperability. Some notable functionalities of Quant include multiple token ledgers along with DLT smart contracts. On top of that, this Layer 3 protocol has entered into partnerships with popular enterprises such as Oracle, Hyperledger, and Nvidia.
Examples of Layer 3 protocols show how important they are to the future of the blockchain space. The combination of Layer 2 scalability solutions with L3 protocols for interoperability can solve fragmentation issues in the crypto space.
Epilogue
Together we learned what Layer 3 is? And why is it necessary in blockchain.
An overview of the basics involved in Layer 3 solutions shows how they can pave the way for the future of blockchain. Interoperability is one of the biggest obstacles to widespread blockchain adoption. At the same time, L3 protocols can help encourage the use of digital assets beyond the borders of financial applications. If blockchain creates ripples in digital transformation, Layer 2 and Layer 3 solutions can help businesses ride the wave of blockchain demand.
The flexibility to move across different blockchain networks and use digital assets seamlessly on each platform could fuel new Layer 3 blockchain projects in the future. Most importantly, the functionalities of existing L3 protocols show the potential to transform the blockchain space with huge fair value benefits in the future.


