What is Frax Finance? Frax Finance is a popular algorithmic stablecoin platform on the Ethereum ecosystem. After being successful in the algorithmic stablecoin segment, the project is developing more products in the Lending segment. In this article, everyone will learn about Frax Finance with me!
What is Frax Finance?
Frax Finance is the name of a Defi project with a variety of products deployed multi-chain. So when talking about Frax Finance, we are talking about an entire ecosystem of Defi products and services, including Frax protocol (Or Frax Finance Protocol), Fraxlend, Fraxswap, stablecoin FRAX,…
Before the introduction of the Frax protocol, stablecoins were divided into three different types:
- Collateralized in fiat, real world assets issued by a non-traditional company/corporation: USDT issued by Tether, USDC issued by Circle or BUSD issued by Paxos.
- Crypto collateral: These are CDP platforms such as Maker DAO which issues DAI, Venus which issues VAI or Parrot which issues PAI.
- Completely algorithmic – No collateral required.
Frax Protocol opens the concept of a 4th type of stablecoin: fractional-algorithmic stablecoin is a Stablecoin with a mechanism to stabilize exchange rates by partly using algorithms, partly backed by other assets.
Currently Frax Protocol is being deployed on Ethereum and 12 other blockchains with 2 stablecoins: FRAX (pegged to USD exchange rate) and FPI (pegged to the US CPI index, not yet launched). The ultimate goal of the Frax protocol is to provide a highly scalable, decentralized cryptocurrency in place of fixed-supply digital assets like BTC.
Frax Finance’s way of building a Web-App, or in other words, what Frax Finance wants to bring to Users: is to provide Defi services on an All-in-one platform, existing on many chains.
With strategic products including:
- FRAX – Stablecoins
- Fraxswap – AMM DEX
- Fraxlend – Lending protocol
Mechanism of Action
The protocol is a two-token system consisting of stablecoin Frax (FRAX) and governance token Frax Share (FXS).
Mortgage mechanism
FRAX was initially fully collateralized by USDC. Then, as the demand for stablecoins increased, the collateralization rate decreased, FRAX was partially collateralized with FXS and USDC. The algorithm part of FRAX is supported by FXS, which operates similarly to the LUNA/UST mechanism.
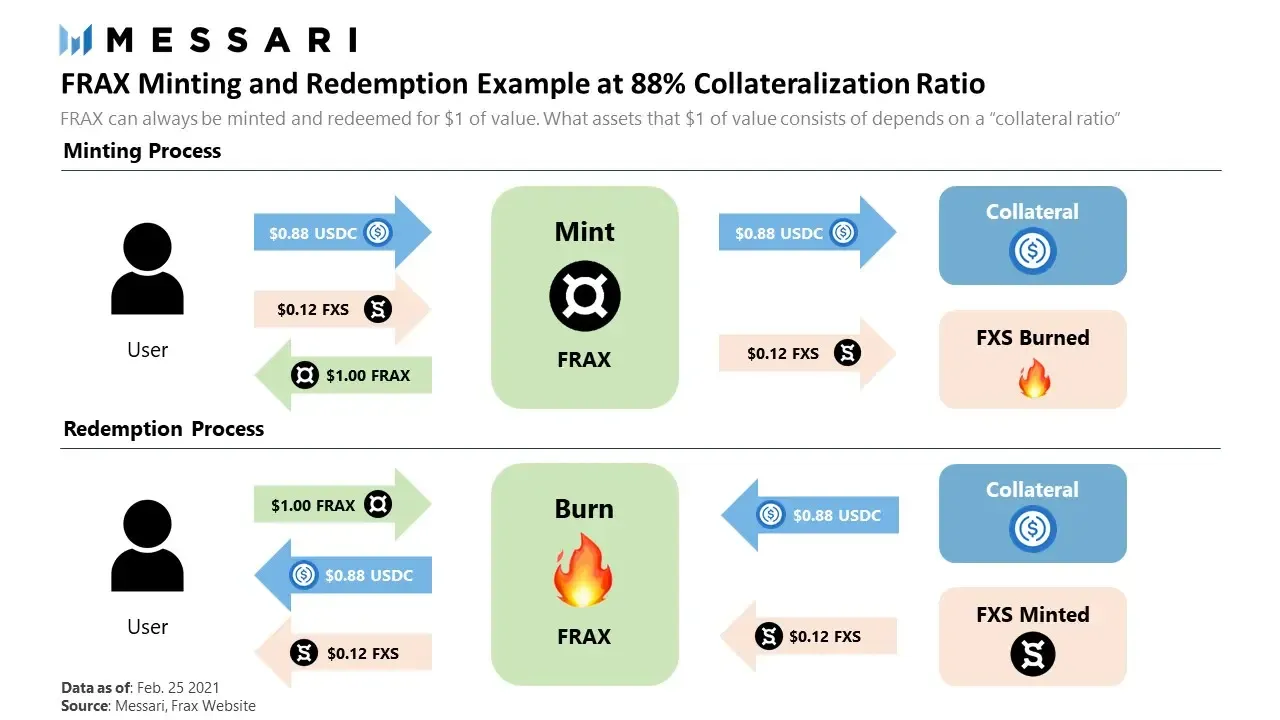
Take the example above to explain the collateral mechanism for FRAX
Frax mint process: User sent 0.88$ USDC and xFXS has a value of $0.12 to the protocol so that its total valuation equals $1. Then 1 unit of FRAX is minted for the user. The FXS portion sent into the protocol will be burned, so the 1 FRAX the user is holding is only backed by 0.88$ USDC.
Mortgage withdrawal process: User sends FRAX back into the protocol for burning. The mint protocol outputs an amount yFXS is valued at exactly $0.12 (y may be different, may be equal to x due to FXS price instability) plus $0.88 USDC is being collateralized and sent back to the user.
That is an example of a process, in reality the ratios are not stable but follow the following system of equations:
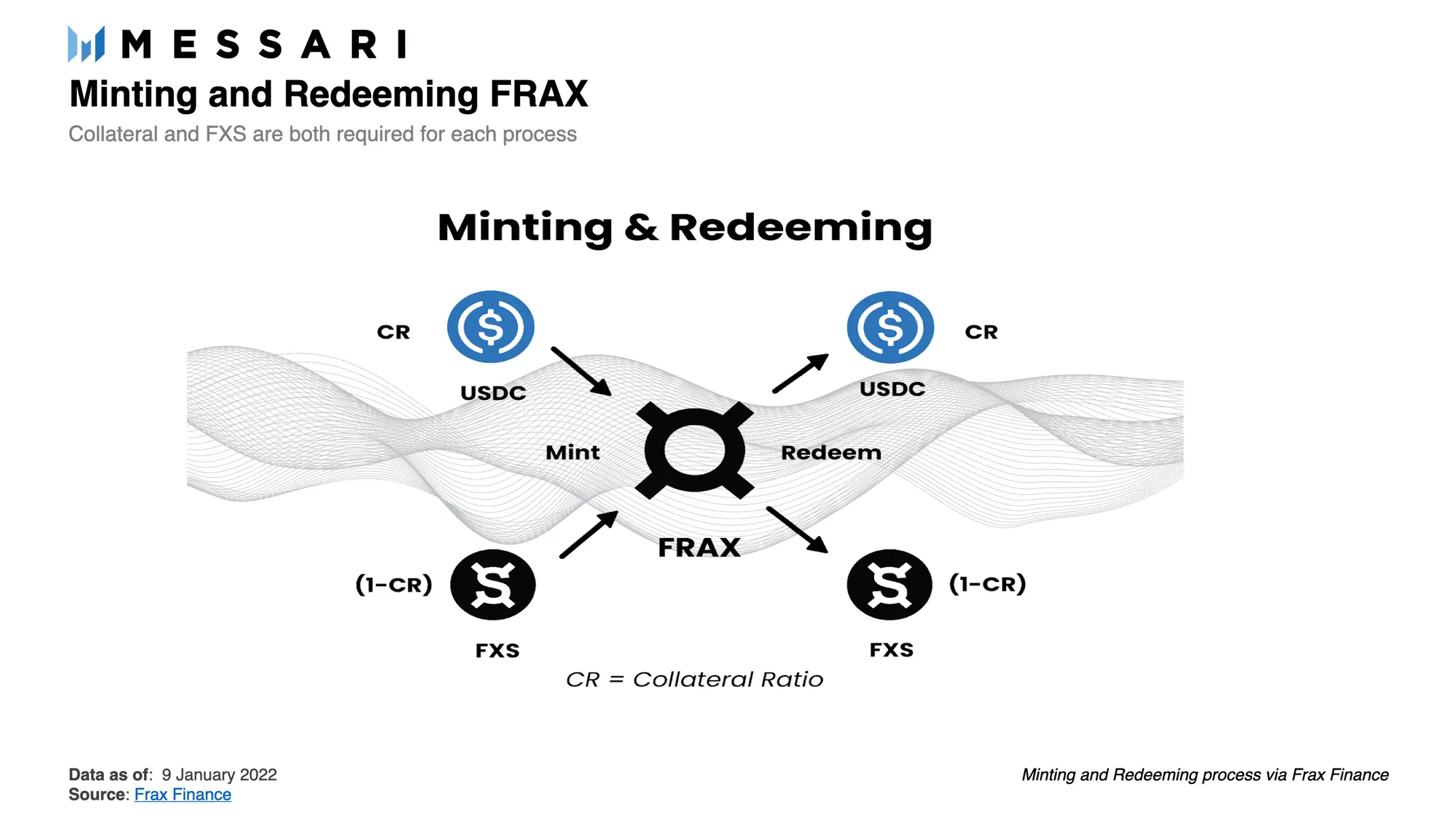
- Where F is the minted FRAX unit
- Y is the USDC unit loaded into the system. Py is the USDC/USD exchange rate
- Z is the FXS unit loaded into the system. Pz is the FXS/USD exchange rate
- Cr is the USDC Collateral Rate
The mortgage mechanism explained above is the premise to explain the exchange rate stabilization mechanism below.
Exchange rate stabilization mechanism
FRAX supply is adjusted to match market supply and demand by targeting the interests of market participants.
Assuming the price of FRAX listed on the secondary market is greater than $1 for any reason, it can be understood that the demand for FRAX is greater than the supply. Provided that FRAX always follows the mortgage rule above, anyone has the opportunity to mint FRAX for $1 and sell it on the secondary market for > $1 to profit from the exchange rate difference. At this time, the FRAX supply is expanded.
When the price of FRAX listed on the secondary market is less than $1, anyone can buy FRAX on it and manipulate the Frax Protocol to withdraw $1 of a mixture of USDC and FXS. FRAX supply is now shrinking, and demand in secondary markets is also increasing, stimulating FRAX to return to the $1 peg price.
This way, FRAX offloads its price fluctuations to the FXS token. This can be good or bad depending on the situation. If the FRAX supply continues to increase, more FXS will be burned, causing deflation in the FXS supply.
“Cumulative value for FXS market cap is the total uncollateralized value of FRAX market cap”
In the first version – Frax v1, the protocol uses an Algorithmic Market Operations (AMO) to achieve stability by: Every 1h if FRAX is greater than $1, Cr (USDC collateral rate) decreases by 0.25%, If FRAX is less than $1, Cr increases by 0.25% to increase the collateral structure in USDC, and Cr remains the same when Frax price = 1.
Frax v2 builds on the idea of AMO in v1 to be designed to run as many AMOs as possible to improve the protocol, increase privacy and capital efficiency while giving more power to FXS holders. This gives the protocol the ability to mint more FRAX when the price is > $1 to bring the price back to $1.
AMOs can be proposed and built publicly by the community but will go through a governance vote before implementation. Currently, there are four AMOs deployed and two more still in development.
The Frax system uses Oracle Chainlink and Uniswap to receive FRAX and FXS collateral price data.
Fraxswap
Fraxswap is Frax Finance’s AMM, core AMM based on Uniswap V2.
Frax Protocol will use Fraxswap to: buy back and burn FXS with profits from AMO, create new FXS to buy back and burn FRAX stablecoins under a price stabilization mechanism, and many other market operations in development.
Fraxlend
To build a complete Defi ecosystem, Frax Finance cannot lack a lending platform – a decentralized capital market. Fraxlend is Frax Finance’s recently launched lending platform.
Fraxlend allows anyone to create liquidity between a pair of ERC-20 tokens, and anyone can create and participate in lending and borrowing activities.
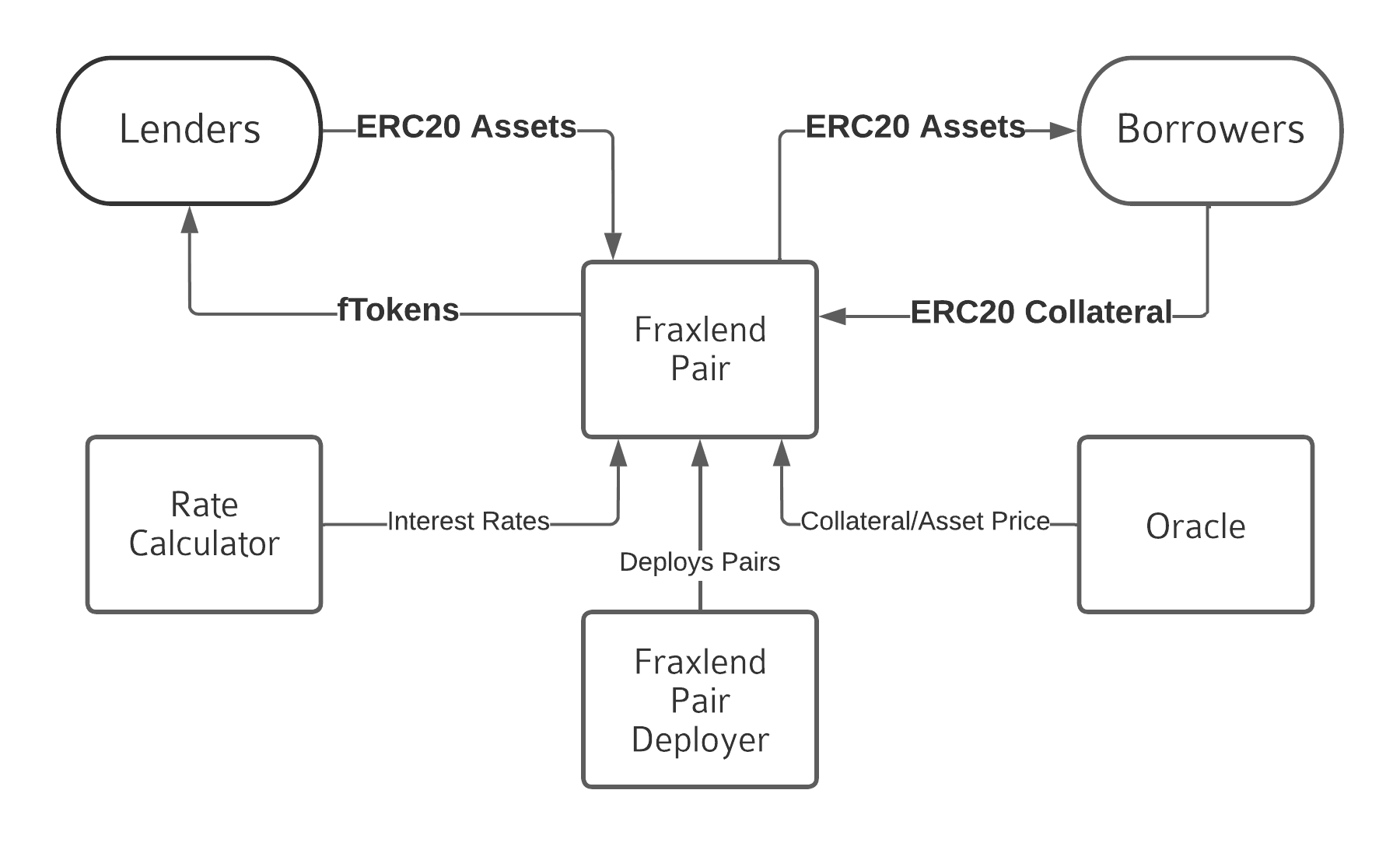
According to the diagram above, the components participating in the lending process on Fraxlend are:
Fraxlend Pair: can be understood as a loan contract, the contract will record collateral and loan assets as ERC20 tokens. Deployed by Fraxlend Pair Deployer is the creator of this asset pair.
Lenders: When Lenders deposit Token Assets into Fraxlend Pair, they will receive interest in fTokens. fTokens can be exchanged for loan tokens.
Borrowers: Borrowers deposit collateral tokens into Fraxlend Pair and receive the right to borrow Token Assets.
Rate Calculator is responsible for determining interest rates.
Each contract relies on one (or two) ChainLink Oracles to determine market rates for both Asset Tokens and Collateral Tokens.
This model is still similar to other lending models in the liquidation mechanism. Each borrower’s position is subject to an LTV that represents the ratio between the value of the asset borrowed and the value of the collateral deposited. LTV changes when the exchange rate between Asset Tokens and Collateral Tokens changes. When the borrower’s LTV (Loan to value) increases above the maximum LTV, the borrower can add collateral or repay the debt to bring the LTV back to the safe range. Otherwise, anyone can repay all or part of the debt on behalf of the borrower and receive the equivalent value of the collateral plus liquidation fees.
How does Fraxlend capture value for Frax Finance?
Lending AMO allows adjusting the FRAX supply on the lending protocol to adjust its interest rate. Therefore, interest rates can be increased to stimulate users to lend to FRAX. This will be an extremely important lever that the protocol can use to generate revenue and make FRAX more available on different chains. Or in short, create more abundant cash flow for Frax Finance.
So in the long term, Fraxlend will be able to bring scalability to the Frax Finance ecosystem to realize the goal of becoming a Defi Ecosystem on every chain.
Although there is a stabilization mechanism that is considered safer than the Algorithmic Stablecoin model like LUNA’s UST, Stablecoins always face the risk of losing peg due to technical errors or use by market participants. Leverage is too high in a bear market.
This is a new product, Frax Fianance in general and Fraxlend in particular are influenced by the FRAX stablecoin – a stablecoin model that is riskier than full-back or over-back stablecoins. So when following Frax Finance or Fraxlend, you should closely monitor the stability of stablecoin FRAX.
Core Team
Frax Finance’s team is mostly the team of old projects such as Everipedia – a Wikipedia Blockchain, DecentralBank.
Investor
Frax Finance’s Backer has the presence of large VCs such as: ParaFi Capital, Mechanism Capital, Dragonfly Capital, Crypto.com Capital, Electric Capital, Multicoin Capital, Galaxy Digital, Tribe Capital, Robot Ventures.
Development Roadmap
Frax Finance’s predecessor, DecentralBank, was built in 2017 and invested $30M by Galaxy Digital to launch on EOS.
- The Frax Finance project started in May 2019.
- December 2020, mainnet protocol on Ethereum mainnet. One hour after launch, TVL in Frax Finance was over $43 million.
- In February 2021, FXS is the Governance token of Frax Finance launching Binance with trading pairs FXS/BTC and FXS/BUSD.
- March 2021, launched Frax v2.
- September 2021, partnered with Pangolin and Frax Finance to launch FRAX on Avalanche.
- December 2021, FRAX partnered with Sacred Finance, Fei Protocol and Alchemix, NearPad to launch FRAX on Near.
- In January 2022, Frax Finance expanded its partnership with Chainlink to bring US CPI data onchain to support FPI
- April 2022 launches Frax V3, a protocol upgrade that empowers veFXS holders to algorithmically control market activity through the expansion and contraction of FRAX supply.
- December 2022 will launch stablecoin FPI and the next step is secondary governance token FPIS.
Tokenomics
Information about Rocket Pool tokens
The Tokenomic of the entire Frax Finance ecosystem is quite complicated because it revolves around 4 main tokens:
- FRAX is a USD-pegged stablecoin. FRAX supply is floating, the supply expansion – contraction mechanism is mentioned in part VI.
- FXS (Frax Share) is the governance token of the entire Frax ecosystem.
- FPI is a stablecoin anchored to the US CPI index.
- FPIS is a secondary governance token.
FPI and FPIS have not yet been launched and the operating mechanism has not been announced. As described by CEO Frax Finance, FPI is designed so that FXS holders will benefit as long as FPI grows, while FPIS supports FPI in price.
Token Allocation
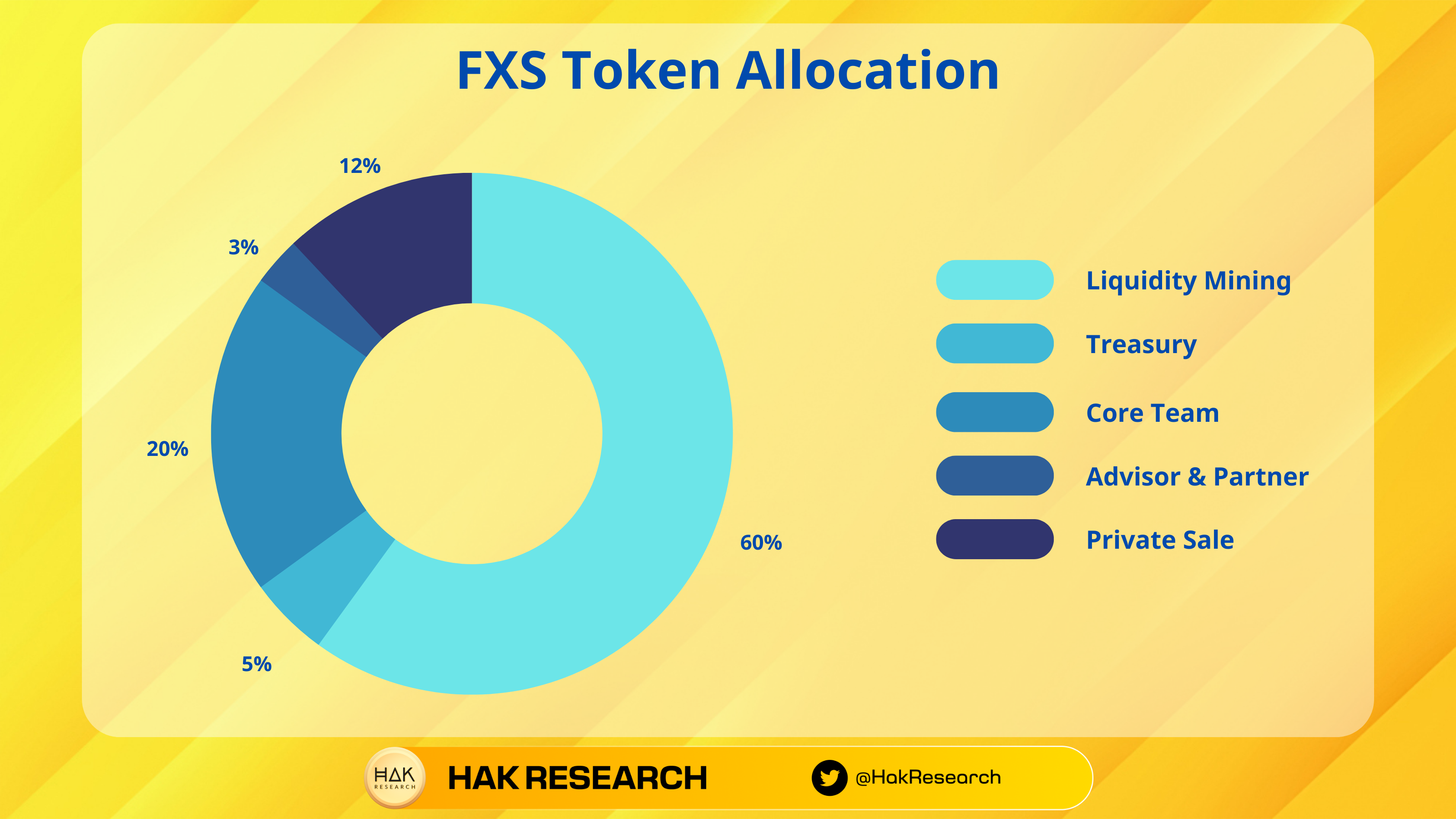
- Liquidity Mining: 60%
- Treasury: 5%
- Core Team/Development Team: 20%
- Advisor & Partner: 3%
- Private Sales: 12%
Exchanges
Currently, FXS is traded on many different exchanges such as Binance, KuCoin, XT.com, BitMart, Sushiswap, Uniswap,…
Information Channel of Frax Finance Project
- Website: https://frax.finance/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/fraxfinance
- Telegram:
Summary
Frax Finance is an outstanding stablecoin project in the crypto market that has gone through many market turbulence but still maintains its peg. However, the mass adoption level of Frax Finance in the crypto market is still relatively low.


