What is DeFi 2.0? DeFi 2.0 is a combination of projects created to overcome the disadvantages of DeFi 1.0 projects. DeFi 2.0 has created a real market fever, although it cannot be as large and influential as DeFi 1.0 did. So in this article, let’s find out what DeFi 2.0 is and what pieces it includes.
To better understand DeFi 2.0, people can refer to some of the articles below:
- Series 3: Real Builder in Winter | Uniswap – The True Unicorn Cryptocurrency Ever Produced
- What is Olympus Knife (OHM, gOHM)? Overview of Cryptocurrency Olympus Dao
What is DeFi 2.0?
The landscape of DeFi and the disadvantages of DeFi 1.0
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) has become a craze in the summer of 2020 that people often remember with the short phrase DeFi Summer. There have been many successful projects such as Uniswap – one of the first AMM platforms, Compound – one of the extremely successful Lending & Borrowing platforms with Liquidity Mining or Maker DAO – a CDP platform that has seen growth. strong.
However, despite its successes, DeFi 1.0 still has weaknesses such as:
- Liquidity: DeFi projects can only maintain a large amount of liquidity when providing Liquidity Providers with a large amount of incentives. When incentives decrease, liquidity also decreases. Clearly, Liquidity Mining has shown its lack of sustainability.
- Decentralizationg: By bringing project development into the community, also known as DAO, but with the development team and investors holding too many tokens, are the projects truly decentralized?
- Security: A lot of DeFi protocols have been hacked & rugpooled. Clearly there needs to be solutions to this problem.
- Efficient use of capital: If people lend BTC or ETH on AAVE, we obviously see very low interest rates, so how can we increase the efficiency of capital use for users? Locked liquidity in the protocol means low capital efficiency.
- Slippage, Impermanent Loss: This is one of the burning problems of DeFi that needs to be resolved as soon as possible.
- Ability of extension: It’s hard to say that the transaction fees on Uniswap, AAVE, Curve Finance,… up to tens of dollars per transaction is a reasonable number.
Obviously, DeFi 1.0 has many problems that need to be solved, but with DeFi 2.0, projects will focus on solving some key issues such as increasing capital efficiency for many types of assets, improving Liquidity Mining often solves Slippage and Impermanent Loss problems.
Overview of DeFi 2.0

DeFi 2.0 was born to solve some of the remaining problems in DeFi 1.0 as I shared above. From the issues above, we have a number of protocols representing the DeFi 2.0 trend such as:
- Olympus KNIFE: With the story of Protocol Own Liquidity, it helps the protocol own liquidity without fear of being withdrawn like protocols using Liquidity Mining. Olympus DAO uses the Bond&ve(3,3) model.
- Abracadabra: A project that utilizes Yield-bearing Tokens as collateral to mint stablecoin MIM. Increase the ability to use capital for users.
- Uniswap V3: The first centralized liquidity model helps LPs optimize profits and users reduce slippage when trading.
- Tokemak: Protocol introduces the concept of Liquidity As A Service. The protocol provides liquidity to other protocols so that other protocols do not need to use LM to bootstrap liquidity.
It can be said that Olympus DAO is the leading project for the DeFi 2.0 movement and there have been many projects to fork the Olympus DAO model such as Temple DAO, Redacted Cartel, Aladin DAO,… and now we will Go into each project’s operating model to see the difference between DeFi 1.0 and DeFi 2.0.
Some Outstanding Projects in the DeFi 2.0 Array
Olympus DAO – Opening the tick trend(3,3)
Olympus DAO is a protocol born with the goal of building a currency (not a stablecoin) owned and managed by the DAO and backed by highly liquid assets called OHM. Some of the notable characteristics of OHM are:
- Fully Collateralized (100% Guaranteed): Every $1 OHM will be backed by $1 of assets in the treasury, it can be DAI, FRAX and there are some proposals to add ETH and BTC as collateral assets .
- Algorithmic Stablecoin (Algorithmic Stablecoin): OHM will not be pegged at a fixed price of $1, but it will be guaranteed by $1 of assets in the treasury. The protocol will manage and govern OHM’s supply.
- Free-floating (Floating price): Because it is not pegged to $1 like other stable coins such as USDT, DAI, etc., the price of the OHM token will be allowed to float on the market and we can see the price of the OHM token at different prices. different.
At that time, OHM’s game was built around Staking – Bond – Tresury and what OHM wanted to target was the tick (3,3) model. At that time, OHM had a staking APY rate of up to thousands of percent, so in order to own OHM, users were required to participate in buying Bond from Olympus DAO. The game begins:
- Step 1: Users will sell liquidity to the Olympus DAO protocol this is the concept Protocol Own Liquidity – Liquidity Ownership Protocol.
- Step 2: The protocol returns OHM users at a discounted price and will vest gradually over a fixed period of time.
The game (3,3) will start here. Users will bring OHM to stake with extremely high interest rates, combined with the project that makes good use of Tresury to earn profits to share with OHM Staker, the profits are so much so the rewards of OHM Staker will continue to be given away by stakers. staking. Thus, the OHM token price will not be dumped even though the APY is extremely high.
Olympus DAO really created a wave when a series of protocols competed to fork the Olympus DAO model such as Temple DAO, Redacted Cartel, Aladin DAO,… but most of those projects failed after a period of time. short time.
However, this model failed when the market went into a downtrend. However, ve(3,3) is still a very important tool for many future development projects.
Uniswap V3 – Changing the game with Centralized Liquidity
Overview of Uniswap

Uniswap is one of the first AMM (Automated Market Maker) platforms built on the Ethereum ecosystem. With Uniswap, users can buy and sell any type of token on the Ethereum network and later on many other EVM Blockchains such as Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, BNB Chain,… without verification or signing. send assets, everything is clear and transparent.
To better understand Uniswap V3, it is best for everyone to have knowledge of Uniswap V1 and Uniswap V2, which I have detailed in the article Series 3: Real Builder in Winter | Uniswap – The True Unicorn Cryptocurrency Ever Produced. Everyone go back and read to understand V1 and V2 then come back to this article.
Problem with Uniswap V2
Uniswap V2 is when Liquidity Providers (LPs) provide liquidity for a certain token pair, by default the LP will provide liquidity for that token from a price of 0 to positive infinity. In a volatile crypto market, this is understandable, especially on DeFi when the number of scam projects is thousands of times higher than real projects.
However, providing prices from 0 to positive infinity for major assets in the market such as BTC, ETH,… seems unnecessary. Obviously, the rate of BTC and ETH falling below $100 in a short period of time is almost impossible, so providing prices for BTC or ETH at prices that are too different from realtime prices is quite redundant. . Therefore, Uniswap V3 was born.
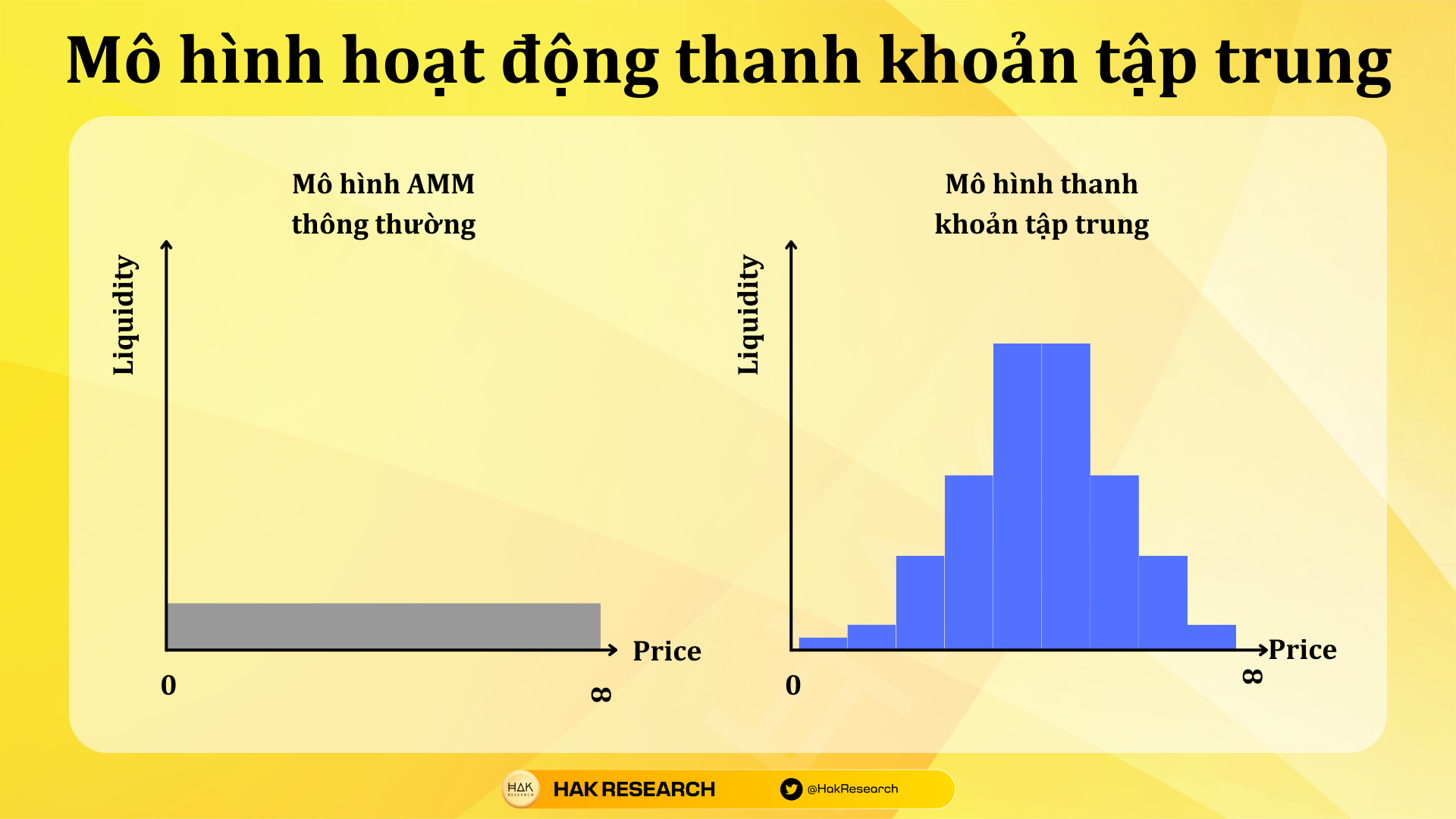
Operating model of Uniswap V2 and V3
With Uniswap V3 there will be some changes as follows:
- LPs will have the right to choose price ranges to be able to provide liquidity. Normally, the price will run in the price range that many LPs analyze the most to choose to provide liquidity. So the liquidity has come to the right place since then slippage and impermanent loss both decreased.
- LP provides liquidity right where the active asset price will receive the highest fee. This is an advantage for both LP and the protocol because when the price line runs LP will change its strategy to match, so liquidity will always be there. highest level no matter what happens.
- Liquidity will no longer be concentrated at levels that are too different from asset prices at real time.
- LPs will have different strategies & analysis, so in every asset price range there will be liquidity.
Clearly, Uniswap V3 has solved some major problems of current AMM projects such as capital efficiency or slippage during transactions or Impermanent Loss while providing liquidity.
Tokemak and the concept of Liquidity As a Service
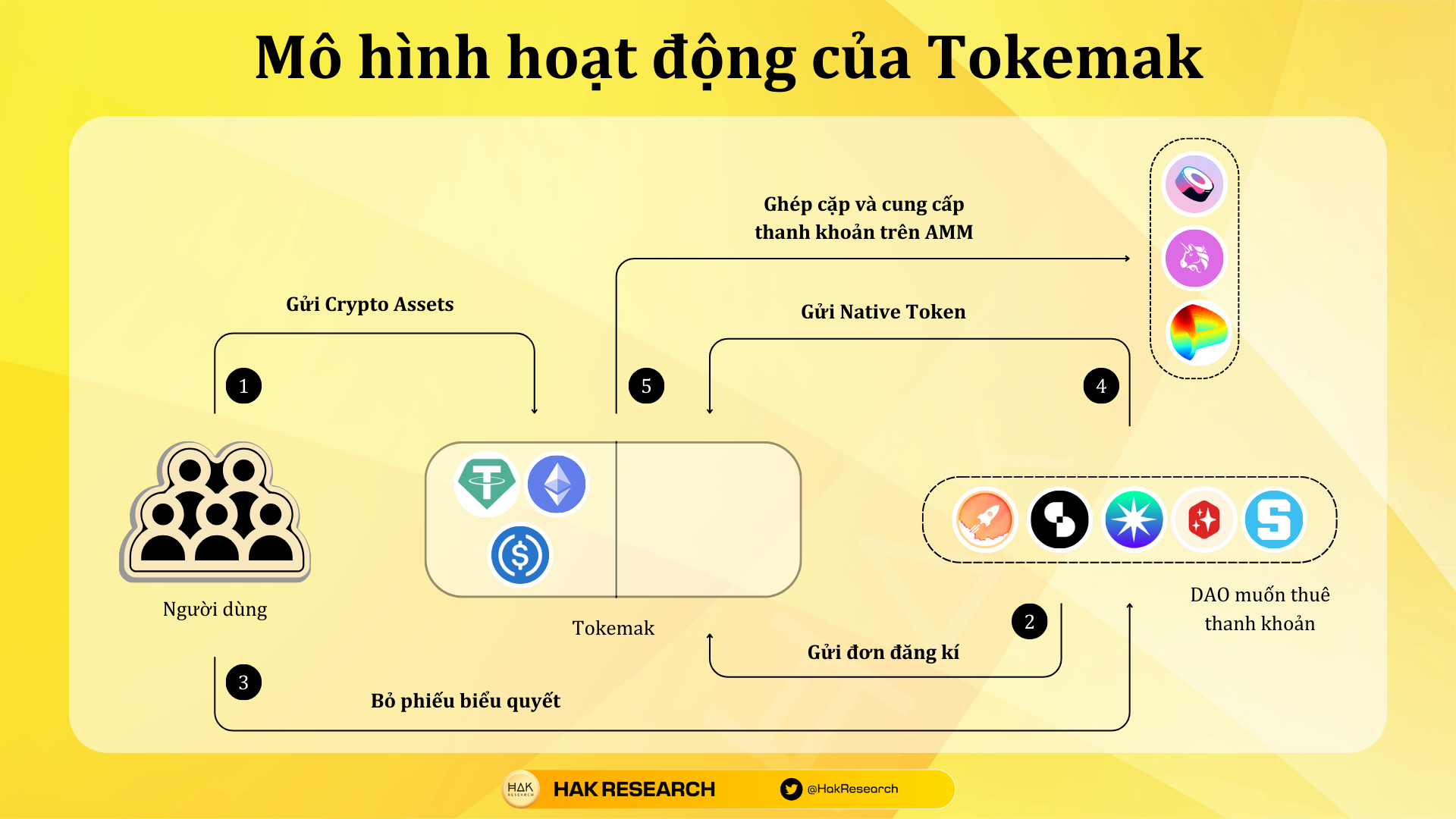
Tokemak is the protocol that invented the concept of Liquidity As a Service. Simply put, it is easy to understand that instead of the project having to give up native tokens to do Liquidity Mining (LM) to bootstrap liquidity for its native token pool, using Using LM has two critical elements:
- LM generates a large amount of tokens into the hands of LPs. LPs can dump native tokens to gain profits, causing the token price to decrease => incentives decrease here, no matter what they do, it will not benefit the project if the native token does not have an internal strength.
- Incentive reduction over time means liquidity is gradually withdrawn over time. Liquidity for native tokens in the long term is still not guaranteed.
So instead of putting themselves in a bad situation, projects can rent liquidity on Tokemak. Tokemak’s mechanism of action is as follows:
- Step 1: Users deposit assets such as ETH, USDC, USDT,… into Toke’s liquidity pools.
- Step 2: Protocols will subscribe to liquidity leases from Tokemak.
- Step 3: The voting war begins and there will be winning projects in renting liquidity from Tokemak.
- Step 4: The protocol sends native tokens to Tokemak and Tokemak gives liquidity which can be ETH or Stablecoin to merge with the project’s native token into 1 pool.
Clearly, Tokemak has partly resolved the problems that existed in DeFi 1.0. However, most of the projects that come to Tokemak are projects that want to develop in the long term, while projects with a short-term vision will still choose the old path.
Abracadabra with the story of optimizing capital utilization
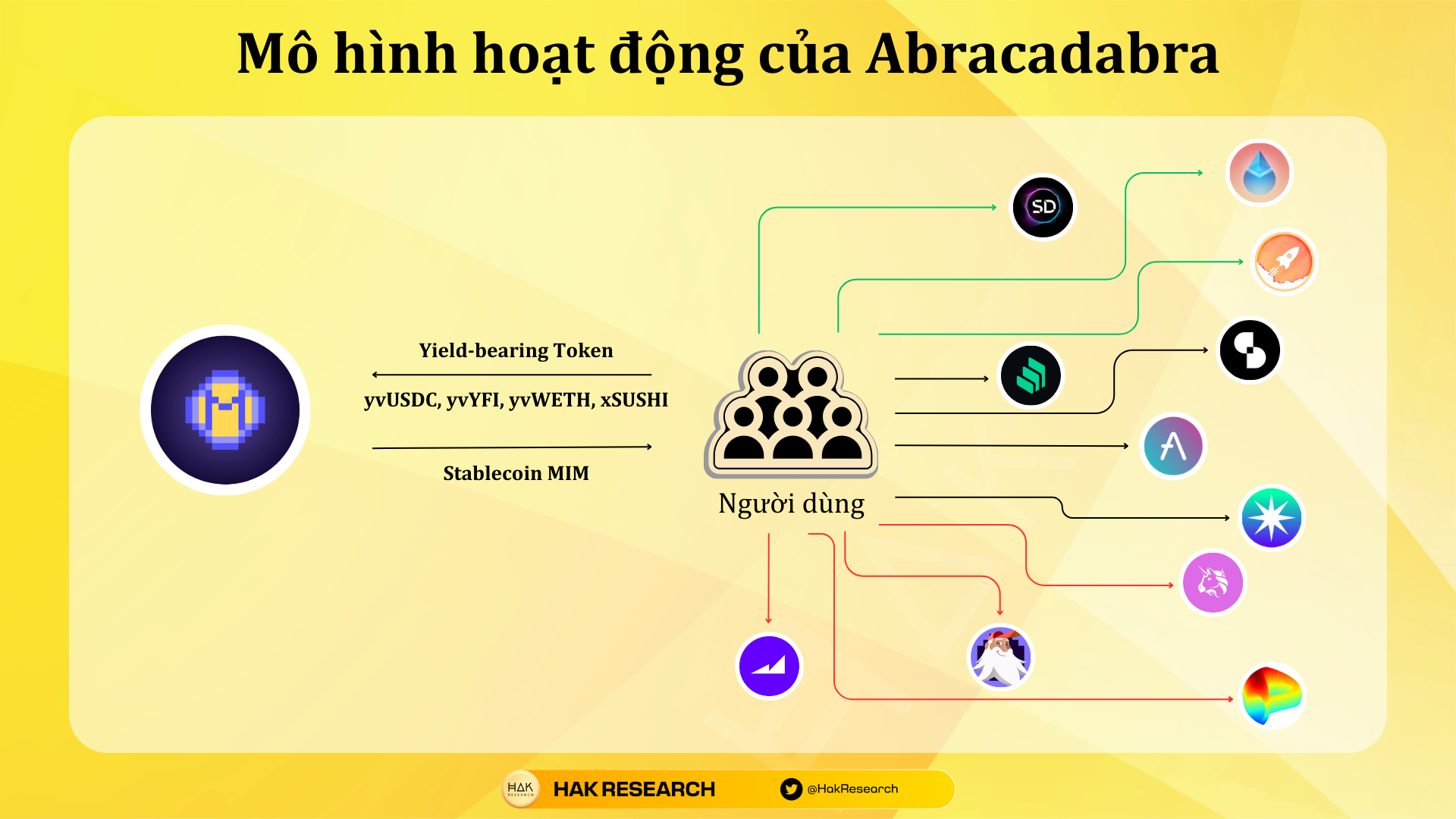
Abracadabra is an All in One DeFi protocol, however to participate in Abracadabra’s ecosystem you need MIM stablecoin, so how to get MIM? Those are the assets you receive when participating in Yield Farming on Yearn Finance such as yvUSDC, yvYFI, yvWETH or some assets like xSUSHI. The above assets are also known as Yield-bearing Tokens.
Yield-bearing Tokens are types of tokens that the protocol returns to users as an asset representing the user’s assets residing in the protocol. Yield-bearing Tokens can be considered as a type of bond that the protocol issues to users.
Abracadabra’s mechanism of action is as follows:
- Step 1: Users deposit their collateral into Cauldrons. Currently, Abracadabra accepts more than 20 collateral assets on Ethereum and operates on many different blockchains.
- Step 2: In the Borrow section you will mint stablecoin MIM.
- Step 3: Use MIM to make profits in DeFi such as staking, yield farming, leverage yield farming,…
Clearly, Abracadabra has solved a major market problem with illiquid assets and optimized the ability to use capital for users.
Some Pros & Cons of DeFi 2.0
Advantages of DeFi 2.0
DeFi 2.0 was born and has certain contributions to the crypto market such as:
- Resolve some outstanding issues regarding capital utilization, slippage, impermanent loss,…
- DeFi 2.0 protocols have truly exploded with skyrocketing TVL, users, revenue,…
- Some models have grown stronger like Uniswap V3 while others remain in a moderate state.
- Creating momentum for DeFi 1.0 forces change after DeFi 2.0, we may see more improved models, perhaps we will have DeFi 3.0 then DeFi 4.0 and then gradually increase.
Disadvantages of DeFi 2.0
Besides the commendable advantages and benefits that DeFi 2.0 brings to users and the market, it also has some of the following disadvantages:
- Although it solves DeFi’s problems, it is not all the problems. There are still many open issues, so DeFi 2.0 is definitely not the Endgame of DeFi.
- The Olympus DAO models themselves failed in the downtrend, forcing the project to choose a new direction for protocol development. Tokemak is also having problems expanding its market.
Summary
DeFi 2.0 and DeFi 2.0 protocols are still developing with new directions or improving problems in their operating model. Can DeFi 2.0 return in the future? Hopefully through this article everyone can understand what DeFi 2.0 is?


