What is Blockchain Trilemma? Blockchain Trilemma, also known as the impossible trinity, includes Security, Decentralization and Security of all existing blockchain platforms. It can be said that Blockchain Trilemma is an eternal problem of crypto, why Blockchain Trilemma is always an eternal problem of crypto, please follow the article below.
To better understand Blockchain Trilemma, people can read some reference articles as follows:
- What is Proof Of Work (POW)? Advantages, Disadvantages and Core Operating Mechanism of Bitcoin
- What is Proof Of Stake (PoS)? Advantages & Disadvantages Compared to Proof Of Work (PoW)
What is Blockchain Trilemma?
Overview of Blockchain Trilemma
Blockchain Trilemma, also known as the Impossible Trinity in Blockchain. Why is it called the Impossible Trinity? Blockchain Trilemma believes that any blockchain cannot balance three factors including decentralization, security and scalability. That means that if any blockchain wants to increase one of the three factors, the other factor will be reduced.
For example:
- If the Bitcoin or Ethereum blockchain wants to improve scalability (increase speed and reduce transaction fees), the Bitcoin network is required to reduce decentralization and the security of the network is also reduced. .
- If Blockchain wants to focus on decentralization and network security, the network’s scalability will be significantly reduced.
A more general example is that in order for Solana’s network to reach such a terrible speed, the configuration of the nodes on the network requires extremely high requirements. Not only that, the link components to run the node must be ordered in advance and not available on the market. Therefore, not everyone can deploy a node on the Solana network, so the Solana network will be able to achieve a level of decentralization.
Another example, when Ethereum is on its way to Ethereum 2.0, it is required to upgrade from PoW to PoS. This is controversial because the community believes that PoS cannot be decentralized but PoW.
The pieces make up the Blockchain Trilemma
Decentralized – Decentralization
Decentralization is the core factor that led to the formation of blockchain and helped make this technology so popular. It can be seen that in life, power is concentrated in a few parties such as banks, companies, large corporations, etc. However, with blockchain, the power of all participants in the network is the same.
Transactions on the blockchain will be guaranteed by a network of nodes, each participating in validating transactions and storing the full version of that blockchain. Therefore, the higher the number of nodes, the more decentralized the blockchain network. The more decentralized the network, the more network security and transparency are enhanced.
Scalability – Scalability
When we talk about blockchain’s scalability, we talk about transaction speed and transaction costs on that network. Normally, users often expect the scalability of blockchains to be at least equal to or greater than international payment platforms such as Visa, Mastercard, Paypal,… It can be said that users expect TPS of Blockchain must be 6 numbers or more.
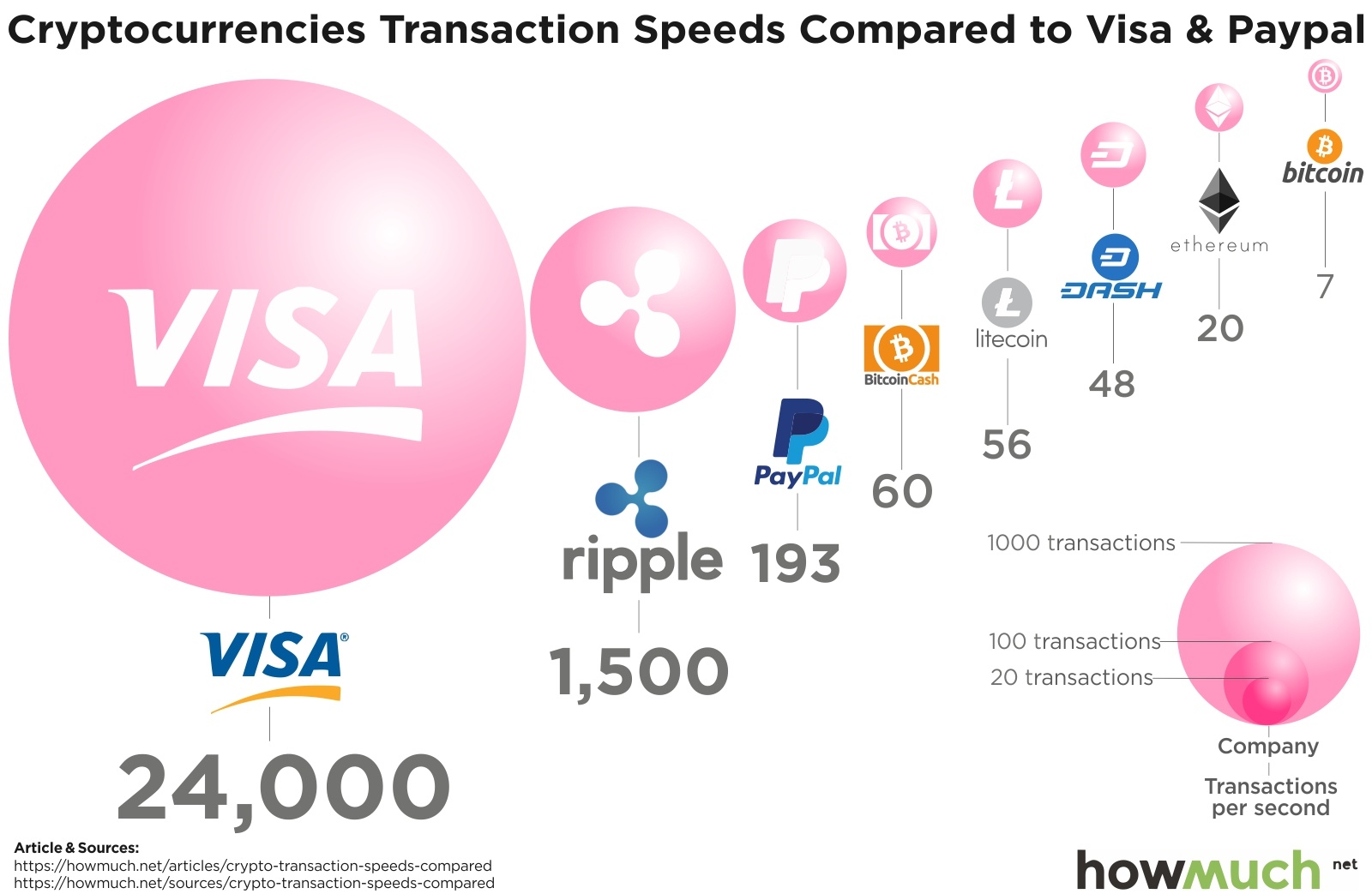
If we make a small comparison between blockchain and traditional payment companies, we see that the scalability of popular blockchains on the market today is far behind. The scalability of Ethereum and Bitcoin is less than 1/20 of Paypal, let alone Visa or Mastercard.
Therefore, many blockchains were born with the goal of achieving hundreds of thousands of TPS with almost zero transaction fees. Some outstanding solutions are as follows:
- Ethereum 2.0: This is Ethereum’s long-term expansion path combined with Danksharding technology that can help this network reach 100K TPS.
- Layer 2: These are short, medium and even long-term solutions that go hand in hand with Ethereum, bringing scalability from 20 – 1000 times compared to Ethereum’s main network.
- Parallel Execution: Is a solution where transactions are executed in parallel to help the blockchain network expand exponentially. Typical projects: Aptos, Sui, Monad, Fuel Labs, Linea,…
- Internet Of Blockchain: Instead of each blockchain performing too many tasks, with the IOB model, each blockchain will choose different strengths to develop and then connect back to each other with a single bridge. Typical projects: Cosmos, Polkadot and Avalanche.
- Modular Blockchain: Separating the consensus and execution process helps the network be more optimized. Typical projects: Celestia, Ethereum 2.0,…
It can be seen that developers are researching and applying many different solutions to solve the scalability problem and each solution has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Security – Security
The security factor can be understood that developers will use algorithms, execution and consensus processes of transactions, etc. to ensure the integrity, safety, and security of the blockchain. That’s guaranteed
- Transactions entered into the blockchain must be transactions that are not subject to fraud by users.
- Transactions, once added to a block and the block entered into the blockchain, cannot be changed. This is the integrity of Blockchain.
Securing the blockchain network is like the state establishing the law to help people live and work according to the law, but if the law is circumvented by certain individuals, the country is certainly not safe. and people will leave their country. Blockchain is similar. It can be said that among the factors, Security is the least mentioned factor in the impossible trinity.
Is it possible to balance Blockchain Trilemma
From my perspective and based on the data I have collected, balancing all three factors above can be said to be impossible, the evidence has shown us:
- Solana achieved great expansion with high TPS and almost zero transaction costs, but the Solana network was shut down many times and many people questioned Solana’s decentralization.
- To achieve high TPS, the BNB Chain network only has a few dozen validators. Obviously, BNB Chain is a company under the cloak of Blockchain. Polygon is also a similar case.
- Ethereum Classic also suffered from 51% attacks many times due to lack of concentration.
From my perspective, one of the best ways to ensure all three factors is Layer 2 and Layer 3 solutions. Layer 1 will be the place to ensure decentralization and security. Meanwhile, Layer 2 and Layer 3 platforms will focus on the implementation element, which can be said to be quite similar to the Modular Blockchain model in the future.
In my opinion, trade-offs are necessary. It is not necessary to be too decentralized or too fast, but we must choose a balanced solution, then a blockchain can be called complete when it neutralizes all three factors.
Summary
Blockchain Trilemma is still a headache for developers in the crypto market. However, I believe that at some point we will have solutions that neutralize all three factors above. Hopefully through this article everyone can understand what Blockchain Trilemma is?


