What is Bitcoin Ordinals? Bitcoin Ordinals is the latest method to create NFTs on Bitcoin that is receiving huge attention from the community recently. So what is special about Bitcoin Ordinals? Let’s find out with Weakhand in this article.
What is Bitcoin Ordinals?
Overview of Bitcoin Ordinals
Released on January 20, 2023 by Casey Rodarmor, Bitcoin Ordinals as the newest method to create NFTs on Bitcoin. Bitcoin Ordinals are created by attaching more information such as images, videos, sounds, etc. to a single satoshi on the original Bitcoin blockchain.
Bitcoin Ordinals uses an arbitrary ordering system called Ordinal Theory (a numbering scheme for Satoshis that allows individual satoshis to be tracked and transferred) to identify each individual Bitcoin satoshi with a unique ID. Because it is completely native to Bitcoin, Bitcoin Ordinals operates without changes to the Bitcoin protocol and without any additional layers.

What is Bitcoin Ordinals
Note: Satoshi (Sats) is the smallest monetary unit of Bitcoin, one bitcoin can be divided into 100,000,000 satoshi.
History of Bitcoin Ordinals
Although, Bitcoin Ordinals were initially created through the concept of Ordinal Theory but today Ordinal NFTs have been made possible thanks to updates Segregated Witness (SegWit) and Taproot for the Bitcoin protocol, taking place in 2017 and 2021 respectively.
It’s worth noting that these updates are not specifically aimed at creating these new types of NFTs. However, as each update has increased the amount of arbitrary data that can be stored on-chain in a block. Users can now store data including images, videos and even games on Bitcoin’s network. So, Ordinal NFTs were accidentally created through these 2 updates.
What is Segregated Witness (SegWit)?
SegWit was a 2017 update to change Bitcoin’s transaction format that improved transaction throughput and increased the size stored in a block, thereby reducing transaction times and speeding up the validation process.
In essence, SegWit reduces the transaction size in each block by dividing a transaction into two parts: The first part contains the wallet addresses of the sender and recipient, and the second part contains “witness data” containing the transaction signature. SegWit removes “witness data” from the main block, significantly reducing transaction size. As a result, transactions require less space, allowing for more transactions per block and significantly increasing the capacity of the Bitcoin network.
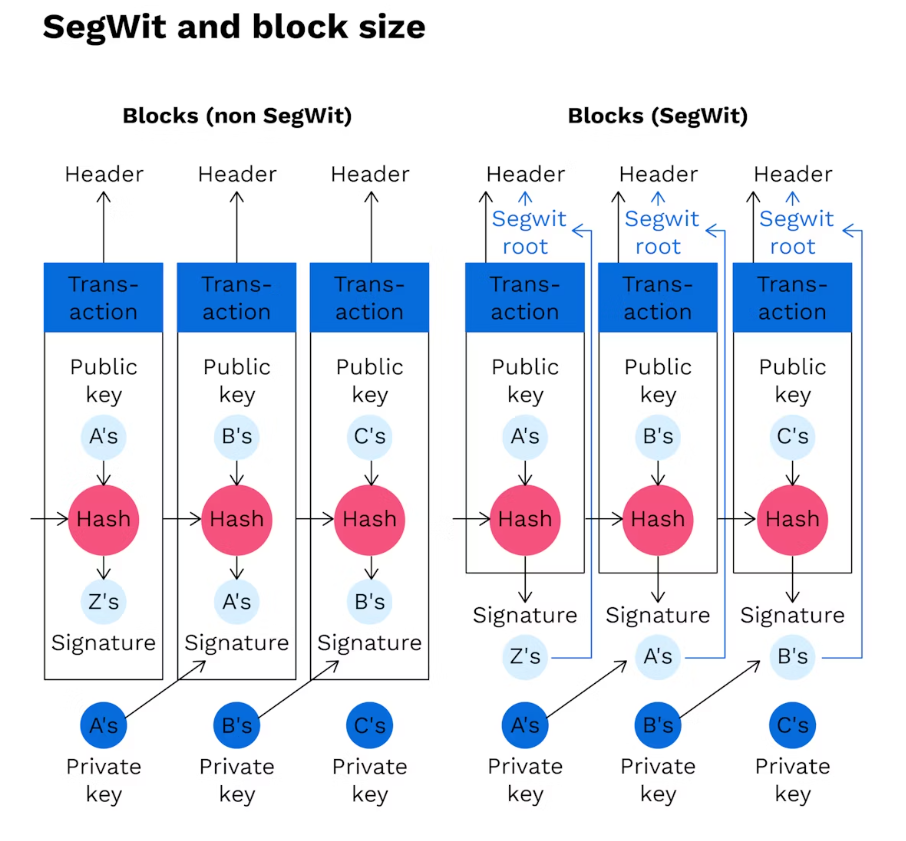
The difference of each Block before and after the SegWit update
What is taproot?
Deployed in November 2021, Taproot is Bitcoin’s latest update that aims to address privacy issues and improve the transaction speed of the Bitcoin network.
The Taproot update includes 3 separate Bitcoin improvement proposals (BIPs) including:
- Schnorr Signatures (BIP340) – facilitates the secure and fast authentication of Bitcoin transactions.
- Taproot (BIP341) – an upgrade to Bitcoin that uses Merkelized Alternative Script Tree (MAST) to reduce data volume and increase privacy.
- Tapscript (BIP342) – a coding language upgrade to Bitcoin Script intended to create smart contracts for the future Bitcoin network.
Overall, Taproot helps reduce the amount of data transmitted and stored on the blockchain, increase the number of transactions per block, and reduce transaction fees. It also improves security by preventing signature modification attacks on Bitcoin transactions before confirmation, which could weaken the integrity of Bitcoin.
How Does Bitcoin Ordinals Work?
Each Bitcoin Ordinals is created through 2 components:
- Ordinal Theory – is the system of arranging sats to create the “Non – Fungible” attribute required for NFTs.
- Inscriptions – the primary content of Ordinals NFTs includes images, text, videos, or any arbitrary data that users consider synonymous with NFTs.
To make it easier to understand, I can make an association of Ordinal Theory and Inscriptions with 2 properties of NFT as follows:
Ordinal Theory is similar to TokenID
TokenID is what makes NFTs unique in terms of functionality. They give each NFT a unique identifier that allows users to distinguish NFTs from each other. For Ordinal Theory provides a numbering system for individual sats. According to Ordinal Theory, satoshis are numbered in the order they were mined with the first being the first satoshi mined since 2008. When a satoshi is transferred, its order is preserved through the system based on a first-in, first-out mechanism based on transaction order.
Inscriptions are similar to Metadata
Metadata is a data file that makes up the content of an NFT. NFT metadata can describe its characteristics and properties such as name, transaction history, characteristics, links to stored images. With Inscriptions, data is stored in the transaction’s witness data. To write data to a specific satoshi and create an Ordinal NFT, users must deposit a separate file to a Taproot-compatible wallet and attach the desired metadata as part of the transaction.
Bitcoin Ordinals Classification
If people don’t know, Bitcoin Ordinals is divided into two types, which are BRC 20 and Ordinals NFT. Initially, Bitcoin Ordinals or it can be called Ordinals NFT is a method of creating NFTs on the Bitcoin blockchain. However, in March 2023, Domo – a Bitcoin developer discovered a new method to create tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain by attaching a text in JSON format to each Satoshi.
Even though it was just an experiment, up to now BRC 20 has become an unexpected success with 2 tokens ORDI and Sats having increased thousands of times and being listed on leading Cex exchanges such as: Binance and OKX, market capitalization. Theirs also reached billions of dollars. Talking about the difference between BRC 20 and Ordinals NFT, it probably only comes from the input data in which Ordinals NFT uses image, video, audio format data,… to insert into each Satoshi and BRC 20. is a text format with a JSON code assigned to each Satoshi. Because they share the same creation method and don’t differ too much, we can consider BRC 20 a variation of Ordinals NFT.
Pros and Cons of Bitcoin Ordinals
Although adopting Bitcoin Ordinals can be beneficial, not everyone agrees with this. In fact, some argue that adding an NFT element to the blockchain goes against Satoshi Nakamoto’s original plans when launching the asset class in 2009. In particular, the developers of Bitcoin Core oppose the use of Ordinals on the view that it is ineffective for Bitcoin applications.
The emergence of Bitcoin Ordinals transactions increases fees and can lead to network congestion. Although, the Bitcoin cryptocurrency community seems divided on the subject, overall Bitcoin Ordinals has brought innovation to the Bitcoin space.
How to create Bitcoin Ordinals
The steps to create a Bitcoin Ordinals are as follows:
Step 1: Use an Ordinals-compatible Bitcoin wallet
Similar to other blockchains such as Ethereum, BNB Chain,… Users need an electronic wallet to store, manage and trade Ordinals NFT. Some popular wallets that users can use include: Hiro Wallet, Xverse wallet, Ordinals wallet, ….
Step 2: Create Bitcoin Ordinals
To create Bitcoin Ordinals, users can use a number of services provided by third parties such as: Gama, Ordinalsbot, Ordswap Inscribe,… Below I will guide everyone to create NFTs using Gama (Save Note: Need to prepare some BTC fees before creating)
1. Select the type of inscription data the user needs to create. Gama provides 3 types of data including: Singer Image, Bulk Images and Text.
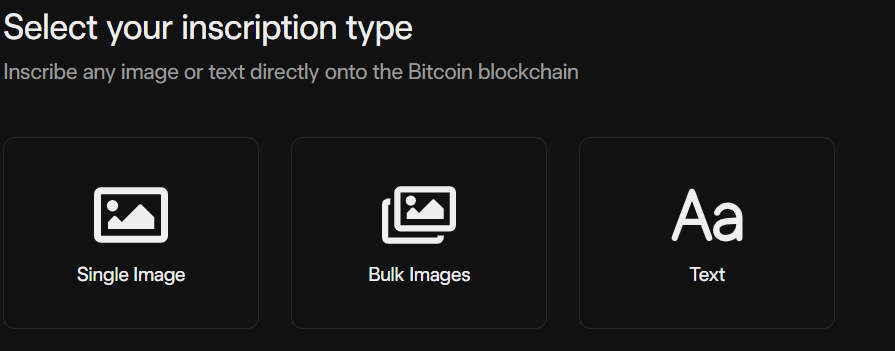
Choose the data type for the NFT
2. If it is an image, everyone can upload the image on the computer
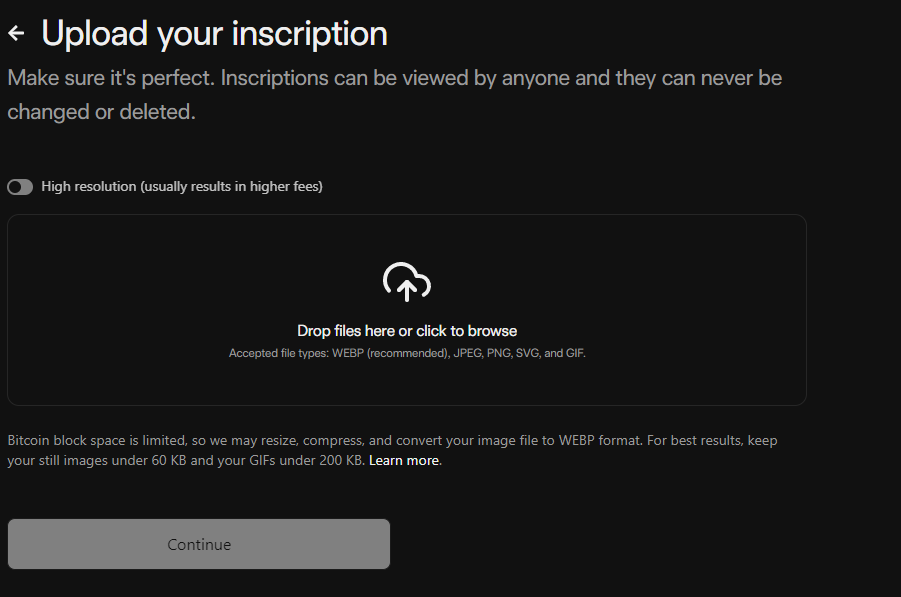
Upload images to Gama
Enter your Inscription
3. Choose the transaction fee, the higher the transaction fee, the sooner Ordinals will be created
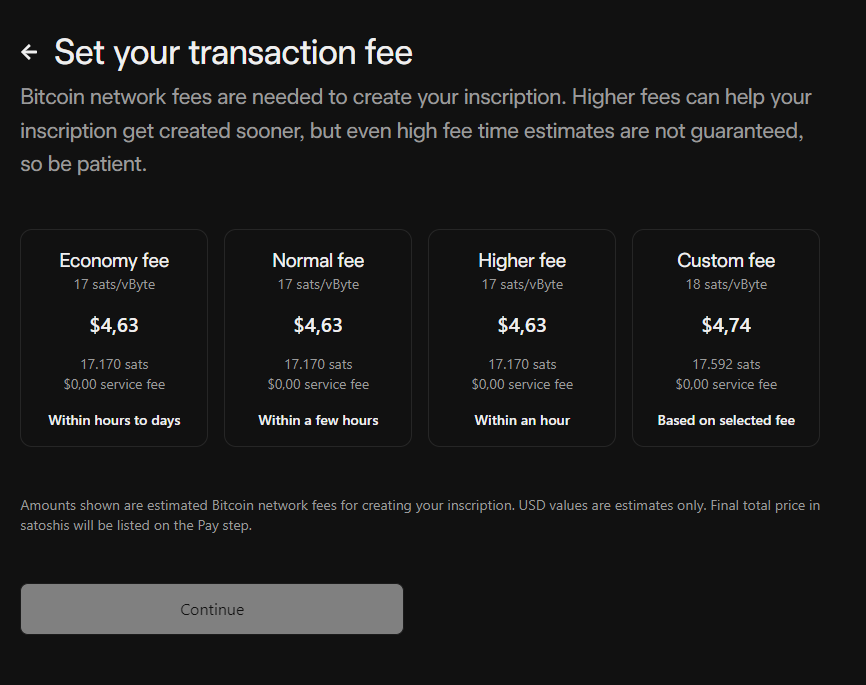
Select transaction fee
4. Enter the Bitcoin Ordinals recipient address, Gamma only sends Bitcoin Ordinals to the Taproot address. Therefore, users need to use BTC wallets that support Taproot addresses like some of the wallets I provide in the first part of the guide.
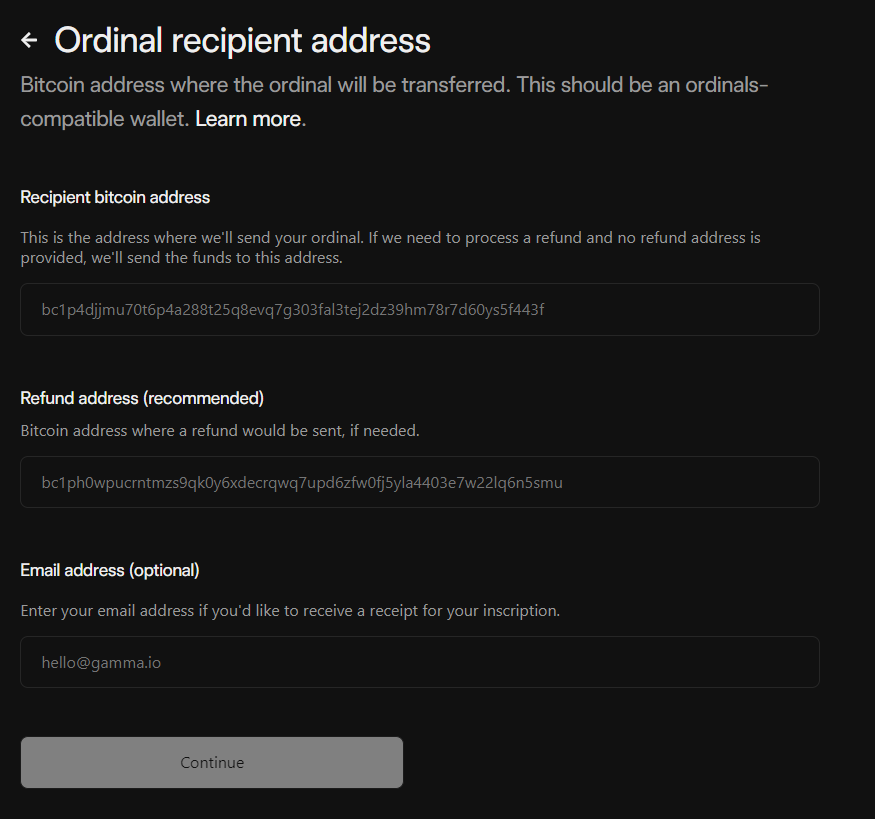
Enter the Ordinals NFT recipient address
5. Pay the transaction fee, with the Economy package selected, users must pay $16.12 USD or 0.00068189 BTC. To pay, users can scan the QR code or transfer money to Gama’s wallet address.
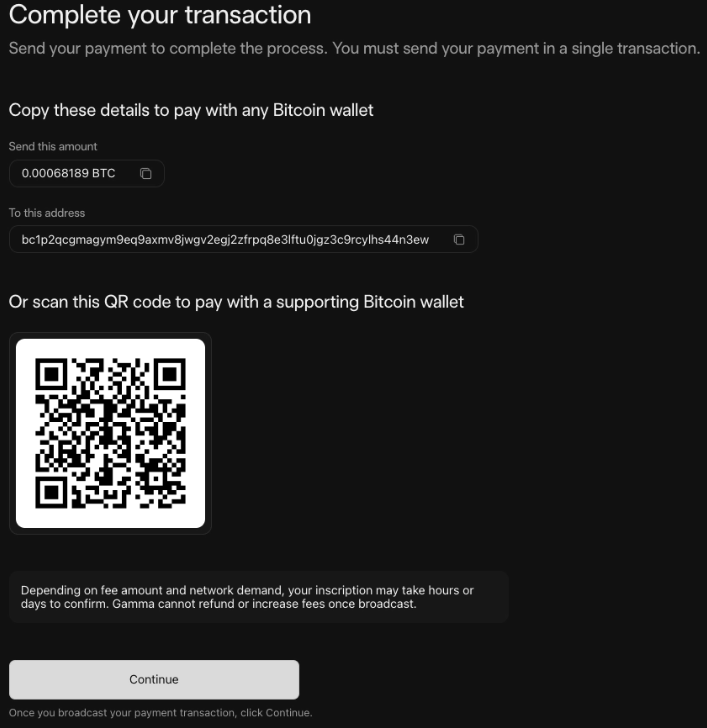
Complete the transaction process
6. Registration status will be notified via the email address provided by the user and completed when Bitcoin Ordinals are sent to the user’s wallet.
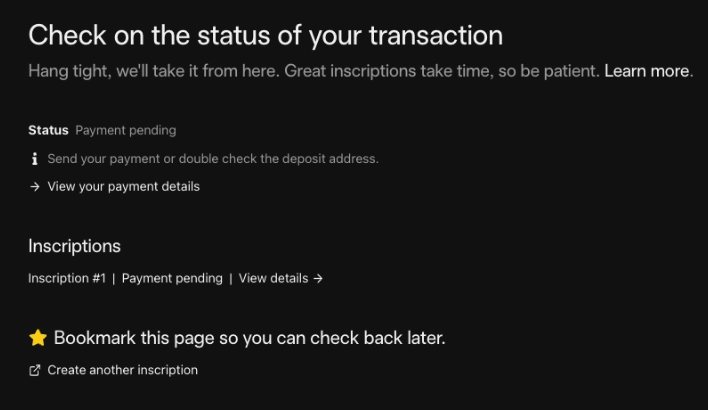
Check registration status
Step 3: Trade Bitcoin Ordinals
Users can trade their Bitcoin Ordinals on e-wallets such as: Xverse Wallet, Hiro Wallet,… or on Marketplaces such as: Magic Eden, Unisat, OKX, ….
summary
Bitcoin Ordinals seems to have created a huge wave of fomo in the community. Over $10M Bitcoin Ordinals have been created with over $43M in transaction fees generated in just a short period of time. Although there are many mixed opinions about Bitcoin Ordinals, this is also a breath of fresh air for the Bitcoin user community.


