Restaking originates from a concept introduced by EigenLayer in improving the liquidity and usability of LST Tokens, and now Restaking is increasingly expanding, gradually becoming a large segment of the Crypto market. So where is the Restaking ecosystem, and what potential pieces does it include? Let’s find out together in the article below.
Restaking & First Concepts
Restaking is set by EigenLayer
Restaking was first introduced by EigenLayer to refer to the act of staking LST Tokens such as stETH, ETHx, rETH, cbETH,… to Validators on the EigenLayer network to get more profits. The question here is why is it called Restaking and how do Validators on the EigenLayer network make profits to share back with the users of the platform.
- Restaking is a combination of 2 words: Repeat and Staking Roughly translated as repeating staking. Here, users first stake their ETH in LSD protocols such as Rocket Pool, Lido Finance, Coinbase or Stader Labs and will receive LST Tokens similar to rETH, stETH, cbETH or ETHx. Users continue to stake these LST Tokens into EigenLayer. That’s why the concept of Restaking was born.
- These LST Tokens will be sent to Validators on the EigenLayer network. Validator’s work on the EigenLayer network is very diverse such as being a data storage layer (DA) for Layer 1 and Layer 2 platforms that need it, being a Sequencer for Layer 2 platforms, being a Light Node for Layer 2 platforms. Bridge platform, making Node for Oracle platforms,…
Operations in EigenLayer
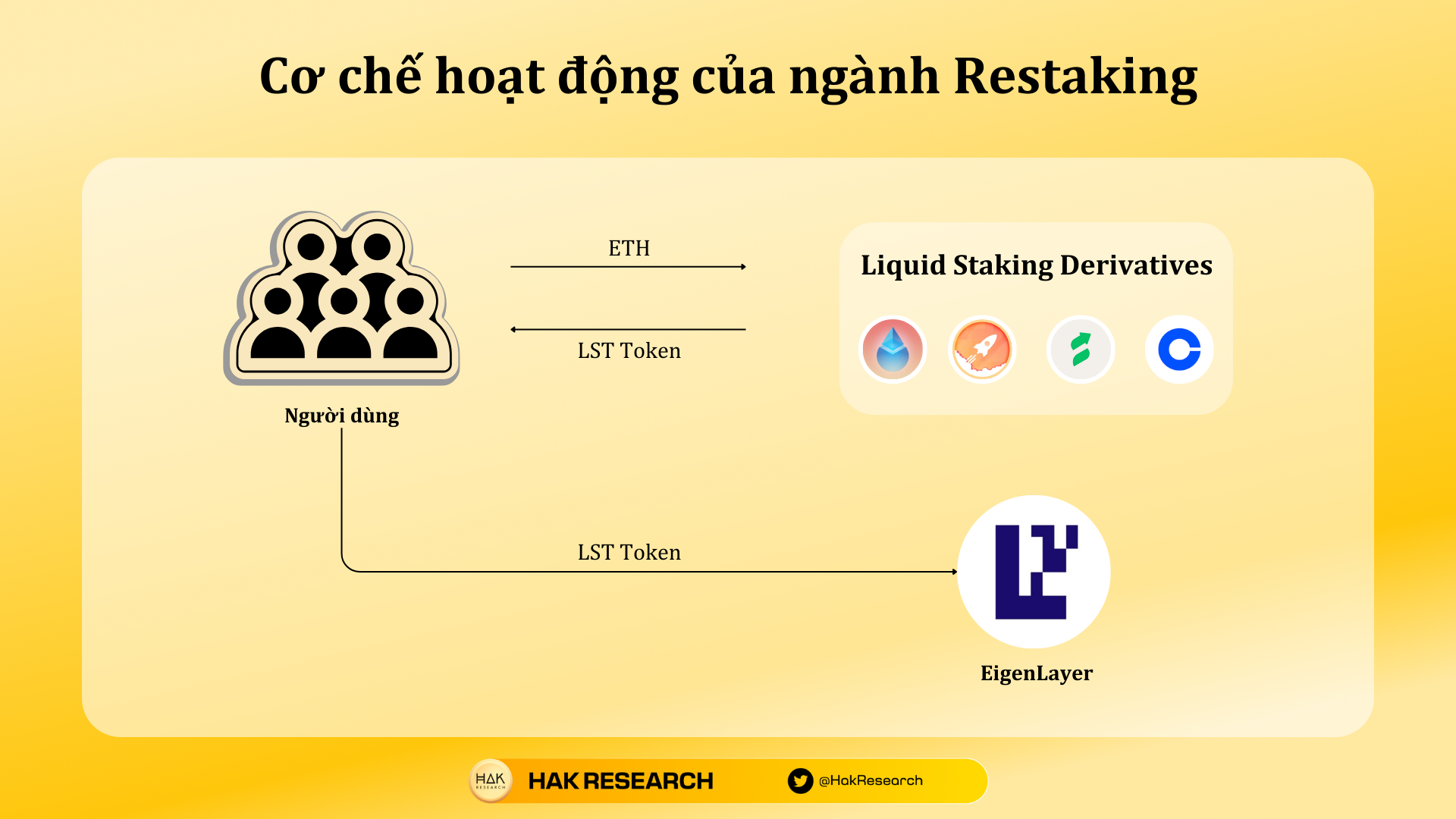
Operational mechanism of the Restaking industry
There are two main activities in EigenLayer coming from the platform’s own users including:
- Users can deposit LST Tokens or ETH into EigenLayer to earn additional profits. This concept is called LSD Restaking.
- Validators on the Ethereum network can reboot to become a Validator on EigenLayer, which means Validators can work on both Ethereum and EigenLayer, thereby increasing profits from one piece of hardware. This concept is called Native Restaking.
Looking at these two operating mechanisms, we can see that it creates a number of problems including:
- For users, their LST Token is locked in EigenLayer, which causes liquidity to be blocked and nothing more can be done. EigenLayer does not issue LP Tokens to its users.
- Becoming a Validator on the Ethereum network and then optimizing profits by running on EigenLayer starts from a large budget of 32 ETH (nearly $70,000 at the time of writing) in addition to hardware requirements. complicated. This also prevents new participants from becoming a Node Operator and making it difficult for the network to move toward decentralization.
When there is a problem, there will certainly be solutions for it. For the first problem, the solution given is Liquid LSD Restaking (or can be shortened as Liquid Restaking) which temporarily translates liquidity to Restaking and Liquid Native Staking for the second issue. We will go deeper into each solution and the outstanding projects in each solution.
EigenLayer Ecosystem Is Increasingly Expanding
Liquid Restaking: Unlocks Restaking liquidity
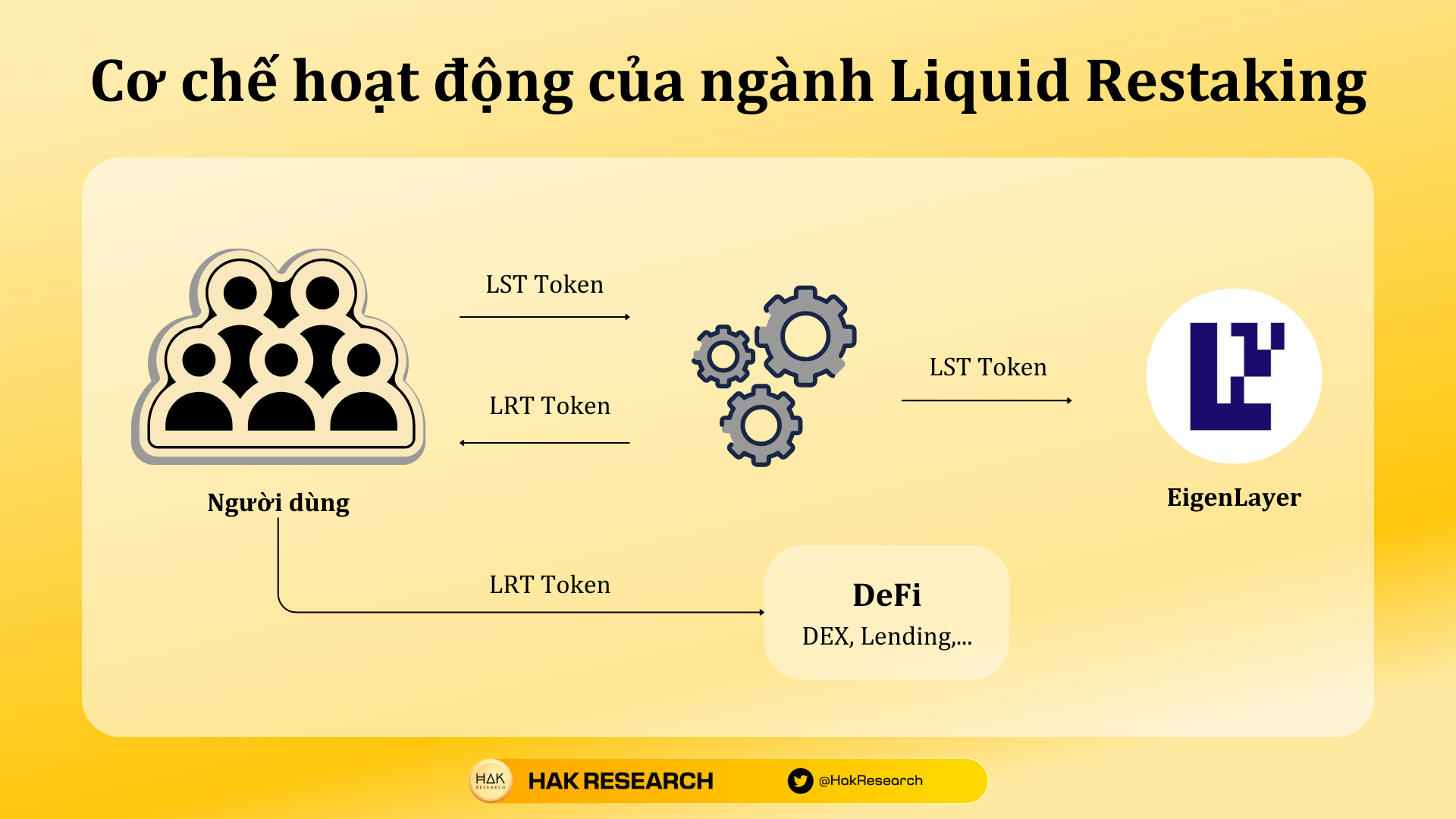
Liquid Restaking mechanism of action
It can be seen that LST Token being locked in EigenLayer is a problem that causes DeFi protocols to continue to innovate to thoroughly solve this problem and Liquid Restaking was born. The working mechanism of Liquid Restaking is as follows:
- After staking ETH on LSD platforms, users will hold LST Token to deposit into the Liquid Restaking protocol.
- The Liquid Restaking protocol will hold the LST Token to stake on EigenLayer.
- The Liquid Restaking protocol will share profits from restaking on EigenLayer and return users a token representing their assets in the protocol.
In fact, this is not a new solution because it is also learning the model of traditional LSD platforms instead of staking directly on the Beacon Chain.
The received token can be called Liquid Restaking Token (LRT). LRT Token can be used to earn more profits in the DeFi market. From here, users will have some profits as follows:
- Profits come from staking ETH on LSD platforms.
- Profits come from the Liquid Restaking platform sharing profits from staking ETh on EigenLayer.
- Profit comes from using LRT Token in DeFi.

Here users can continue to use leverage to maximize profits such as LRT will be a Token based on ETH so it can be used as collateral on Lending & Borrowing platforms to borrow ETH. Then the user continues to hold ETH to stake on LSD and hold LST Token to deposit into the Liquid Restaking platform, repeating. This will be the solution that brings maximum profits to users.
In the context that the Lending & Borrowing protocol does not yet accept LRT Token as collateral, users can buy and sell it on DEXs.
However, it will also open up many risks that users must confront such as:
- Producing too much LRT and LST makes the fraction liquid. Liquidity can easily lead to depeg. If depeg occurs, assets in the Lending & Borrowing platforms will be liquidated.
- Excessive use of DeFi protocols and activities that can take place on Sidechain or Layer 2 platforms also increase the risk of being attacked by Hackers.
Liquid Native Staking: Solution for Node Operators
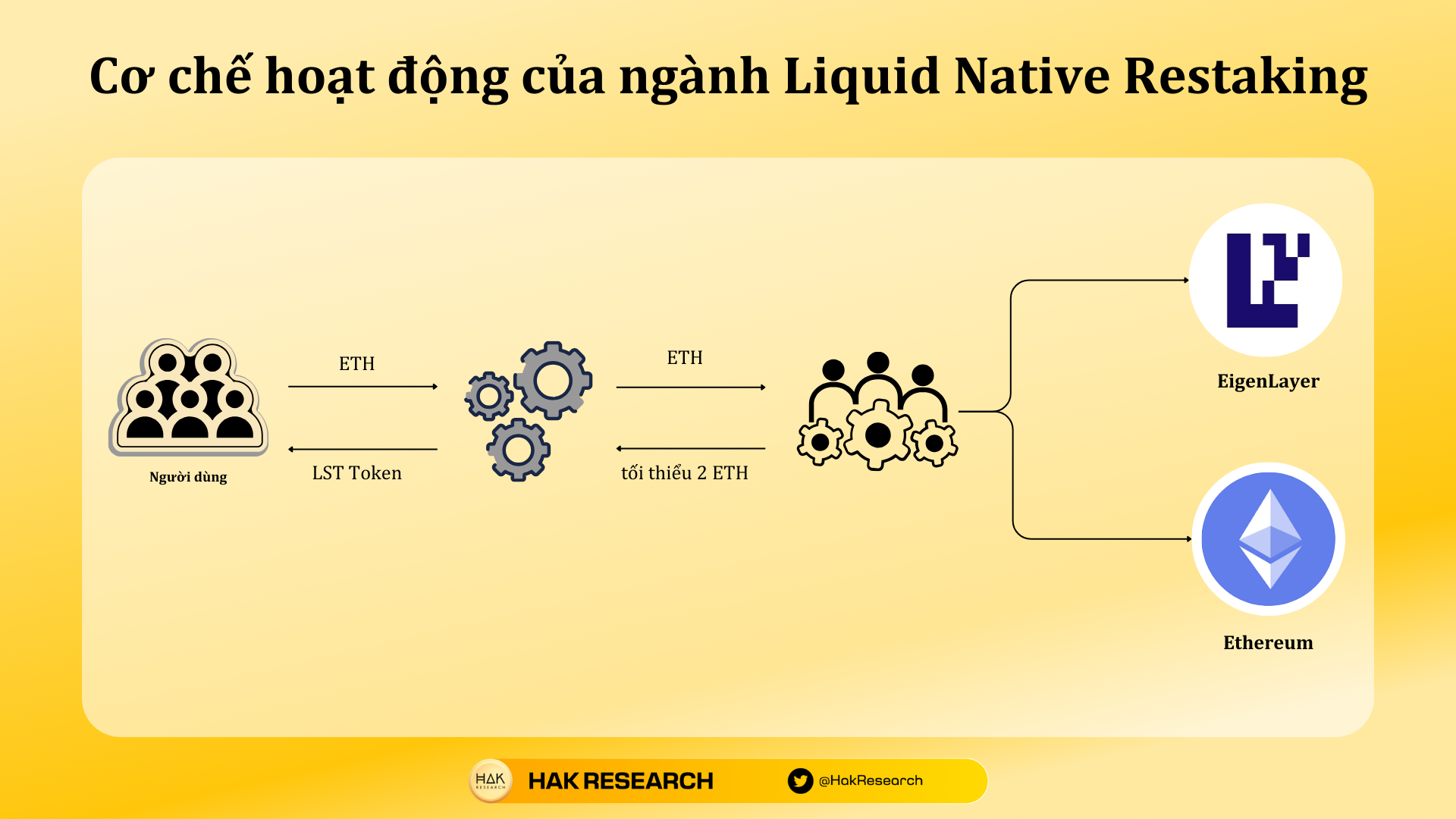
Operational mechanism of the Liquid Native Retaking industry
Normally, when becoming a Node Operator on the Ethereum network, there will be a few main problems as follows:
- The minimum ETH amount of 32 ETH is still a large number for any individual who wants to become a Node Operator on the network.
- Node Operator’s profits are contained in activities on the Ethereum network.
- Easy to encounter off-the-shelf problems, especially slashing, leading to fines for the amount of ETH pledged. It is possible to lose part or all of ETH.
Liquid Native Staking solutions were born to solve this problem. First, the nature of Liquid Native Staking platforms is still Liquid Staking when receiving ETH from users, when enough ETH will be transferred to Node Operators and they will deploy Node on the Ethereum network to make profits. In particular, Node Operators only need to spend about 2 ETH to deploy a Node on Ethereum.
Next, to optimize profits, Node Operators will be deployed on EigenLayer to do work thereby generating more profits. From here, Node Operators’ profits come from activities on Ethereum and EigenLayer. As EigenLayer grows larger, the more services it receives from third parties, the greater the Node Operators’ profits will be.
Not only that, to help operate a Node effectively, Liquid Native Staking solutions also provide additional solutions to help Node Operators avoid errors during operation and increase security such as:
- Ether.fi uses Obol’s DVT technology to help Node Operators secure their assets and can operate a Node without the need for hardware.
- Puffer Finance uses Secure-Signer technology to increase security for Node Operators and in the future will apply Fractal DVT technology to solve hardware problems.
Liquid Native Staking projects also return to users LNS Tokens representing the assets in the protocol. LNS Tokens will carry both the profits of ETH staking on Ethereum and profitable operations on EigenLayer.
Summary
The Restaking industry in general and the EigenLayer ecosystem are increasingly growing. There is a high possibility that when EigenLayer goes into official operation, it will open a new trend for the Crypto market.


