Uniswap and Sushi have both proven that decentralized exchanges can beat Coinbase and other centralized exchanges in a competitive market with many major players.
Nhung Curve Finance (CRV), a decentralized exchange for stablecoins, represents something completely different. It allows for fast, efficient and low-risk stablecoin swaps and proves that decentralized currency exchange is not only possible but also much better than traditional foreign exchange.
So what is CRV and how does Curve Finance work? Let’s continue to find out below!
What is Curve Finance (CRV)?
Curve is an AMM platform that has many similarities with Uniswap and Balancer but the difference is that it only provides liquidity pools is made up of assets that behave similarly to stablecoin or wrapped versions of similar assets wBTC and tBTC . This approach allows Curve to use more efficient, cost-effective, slippage and algorithms impermanent loss lowest of any decentralized exchange (DEX) on Ethereum.
The Curve Finance protocol also contains the Curve token called CRV. It is mainly used to incentivize liquidity providers on their platforms and attract as many users as possible to participate in the governance of the protocol.
The amount of liquidity that Curve provides allows other DeFi applications uses Curve as part of their ecosystem. Applications such as Yearn Finance and Compound Use Curve as one farming solutions in their ecosystem.
Let’s start with a quick introduction to how AMMs work and then we can focus on how Curve achieves lower risk and higher efficiency compared to other AMMs in the DeFi ecosystem.
Operating Mechanism of Automatic Market Makers (AMA)
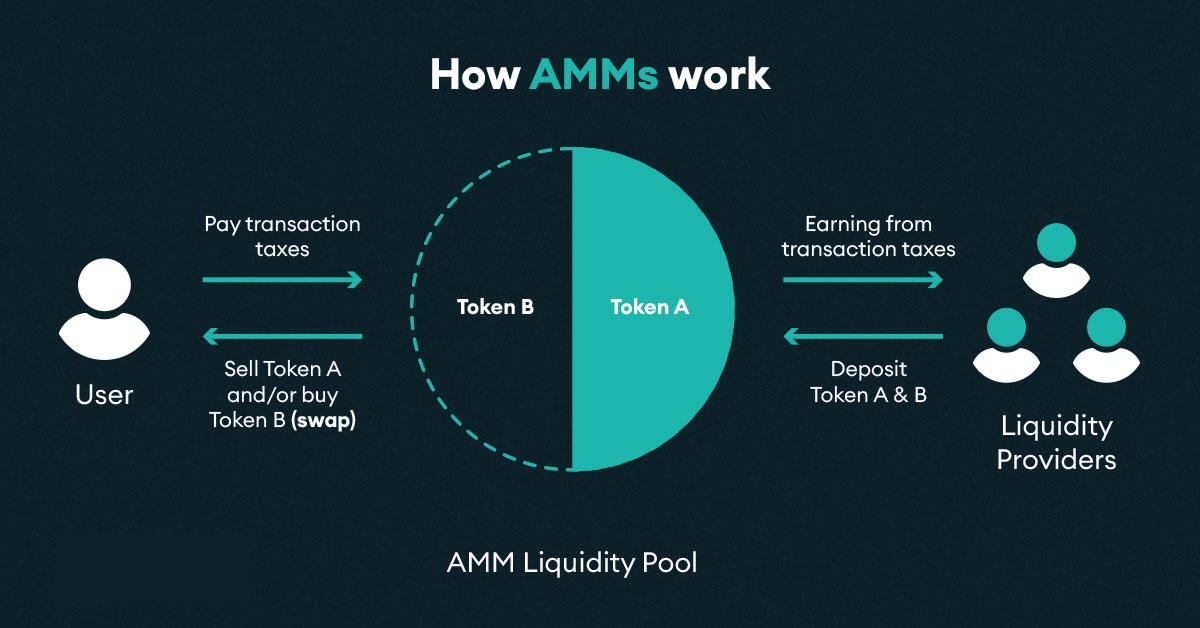
Automatic Market Makers allows digital assets to be traded automatically and permissionlessly using liquidity pools instead of transactions between buyers and sellers. At its core, a liquidity pool is a shared pool of tokens. Users provide liquidity pools with tokens, and the price of the tokens in the pool is determined by a mathematical formula.
By adjusting the formula, the liquidity pool can be optimized for different purposes. Anyone with an internet connection and a number ERC-20 tokens can all become liquidity provider by providing tokens to AMM’s liquidity pool. Liquidity providers typically earn a fee (paid by traders interacting with the liquidity pool) for providing tokens to the pool.
Stable Liquidity Pools
Curve was launched in 2020 with the aim of creating an AMM exchange with low fees for traders, while providing an economical solution fiat currency efficient for liquidity providers. By focusing on stablecoins, Curve allows investors to avoid more volatile crypto assets while still earning high interest rates from lending protocols. Compared to other AMM platforms, the Curve model is especially conservative in that it avoids volatility and speculation in favor of stability.
On AMMs like Curve, liquidity pools are constantly trying to “buy low” and “sell high.” Here are the details on how that rebalancing works, this time with USD-pegged stablecoins: USD Coin (USDC) and TOUGH . If you are selling DAI on Curve, you will trigger the following chain of events:
- More DAI is added to the pool
- The pool becomes unbalanced because there is now more DAI than USDC
- The pool sells DAI at a slight discount to USDC to incentivize balances
- The pool rebalances the DAI ratio against USDC
By selling DAI at a discount, oool is trying to restore the pool to its original state. Because the assets in the Curve pool are price stable with each other, trading between them causes minimal volatility compared to other AMM liquidity pools. On AMMs like Uniswap or Balancer, where liquidity pools can be made up of any token, volatility is high. By limiting the pools and asset types within each pool, Curve minimizes liquidation loss, an AMM phenomenon in which liquidity providers lose token value relative to that token’s market value, due to fluctuations in the liquidity pool.
However, asset volatility is not always negative. Volatility and slippage providing an opportunity for users trying to profit from entering and exiting the liquidity pool at the right time. By trading off the high-risk — and sometimes high-reward — aspect of volatility, Curve instead attracts liquidity providers using what is known as DeFi composability. This means you can use what you invested on the Curve platform to earn rewards elsewhere in the DeFi ecosystem.
Unlike Uniswap or Balancer, Curve does not attempt to keep the values held in different assets always equal or proportional to each other (i.e. balanced). This allows Curve to concentrate liquidity near the ideal price for similarly priced assets (at a 1:1 ratio) to get liquidity where it is needed most. Therefore, Curve can achieve much higher liquidity utilization than those assets.
The same asset approach to AMM is not limited to stablecoins. Versions bitcoin (BTC) encrypted as wBTC and renBTC also make up Curve’s liquidity pools. Compared to stablecoins, bitcoin is highly volatile, but the Curve method still works because tokens in the Curve pool don’t need to be stable — they just need to be stable relative to other tokens in the same pool. In other words, wBTC and renBTC could be in the same Curve liquidity pool, while wBTC and USDC would not be a functional pool.
Composability: Incentivizing Liquidity Providers
On an AMM exchange such as Uniswap, you can earn fees whenever a trade is made. On Curve, transaction fees are lower than on Uniswap, but you can also earn rewards outside of Curve with interoperable tokens.
For example: When DAI is lent on the platform Compound it will be exchanged for a liquid token called cDAI, which will automatically accrue interest to the holder. Holding cDAI means you have the right to withdraw DAI from Compound plus interest. Curve users can use cDAI in its liquidity pool, thus achieving a second layer of utility and earning potential from the same investment.
Usability cTokens of Compound on Curve illustrates the benefits of composability in the DeFi ecosystem. And Compound is just one example of an external DeFi protocol that Curve integrates with. This protocol also integrates with Yearn Finance and Synthetix to maximize incentives for liquidity providers.
CRV Tokens

In August 2020, the Curve protocol began its journey towards decentralized governance by launching a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) to manage changes to the protocol. Most DAOs are controlled by governance tokens that provide voting rights to token holders. In this case, Curve DAO is controlled by CRV tokens .
CRV tokens can be purchased as well as earned through yield farming — when you deposit assets into the liquidity pool and earn tokens as rewards. By providing DAI to the designated Curve liquidity pool, you earn CRV tokens along with fees and interest. Yield farming of the CRV token increases the incentive to become a Curve liquidity provider, as you not only receive financial assets but also ownership of a powerful DeFi protocol.
Anyone with a minimum amount of CRV tokens is affected key to vote can suggest updates to the Curve protocol. Updates may include fee changes, changing where fees are charged, creating new liquidity pools, and adjusting yield farming rewards. Holders vote to reject or accept the proposal by locking CRV tokens. The longer the CRV token is locked, the more voting rights it has.
Summary
Curve is one of the most popular platforms in DeFi because it prioritizes stability and composability over volatility and speculation. Its composable elements make it an interconnected hub of the DeFi ecosystem, and with the CRV token as its governance mechanism, it is a decentralized belongs specifically to its users.


