What is Modular Blockchain? Modular Blockchain is considered Blockchain 2.0 in the crypto market and is considered the future trend of Blockchain in general. So why is Modular Blockchain considered a future trend? Let’s find out together through this article!
Factors That Make Up A Transaction In Blockchain
Execution
This is the execution process shown by how users interact with Smart Contracts such as Swap, Lending, Borrowing, Staking, Trading, Farming,… Besides, it can be the movement of tokens between other wallets. together.
Settlement (Verification & Dispute Resolution)
Settlement is the process of confirming and completing a transaction. This process includes verifying transaction information, confirming ownership of related assets, updating the state of the Blockchain and resolving disputes that arise during transactions.
In Public Blockchain systems, Settlement is performed by nodes in the network. Nodes will verify the transaction information, including the sender’s address, the recipient’s address, the amount of assets traded, and the sender’s signature. If the transaction is valid, it will be added to a new Block. This block will be added to the Blockchain and the transaction will be considered complete.
Normally Settlement Layer does not exist in Monolithic Blockchain and is an optional layer in Modular Blockchain.
Consensus (Consensus mechanism)
Consensus is a mechanism to ensure that nodes in the network agree on the state of the Blockchain. This mechanism needs to ensure that the Blockchain is not illegally altered and that transactions are carried out correctly.
Some consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS) or Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS),…
Data Availability
Data Availability is the ability to ensure that all nodes in the network can access all data stored on the Blockchain. This is important to ensure the security and trustworthiness of the Blockchain, as it prevents malicious parties from attempting to change or delete data.
The Difference Between Modular Blockchain and Monolithic Blockchain
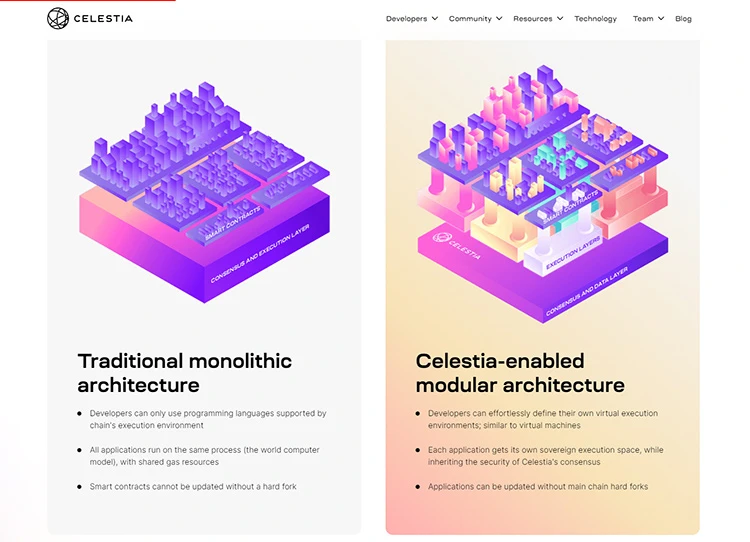
What is Monolithic Blockchain?
Monolithic Blockchain is also known as monolithic Blockchain and the very simple definition is that all the elements surrounding a transaction such as Execution, Consensus and Data Availability all take place on the Blockchain.
Representing Monolithic Blockchain are Ethereum, Near Protocol, Solana, Aptos,…
What is Modular Blockchain?
Modular Blockchain goes in a different direction as it divides the work around a transaction to be processed in different places.
A simple example:
In the process of making a car, there are many different stages. If a group of workers must do all the work to create a car, that company is considered Monolithic Blockchain. But if that company is divided into many different departments, each department is in charge of one stage of car production, then that company is called Modular Blockchain.
Representing Modular Blockchain is Ethereum after completing Sharding, Celestia – the person who laid the foundation for the definition of Modular Blockchain,…
Why is it necessary to advance to Modular Blockchain?
The issues on Monolithic Blockchains we have seen frequently are:
- Solana only runs at a speed of about 3,000 TPS and crashes frequently, while Master Card or Visa have an average TPS of about 25,000 TPS.
- Near Protocol is still in the process of being built and the speed is not too fast.
- Internet Of Blockchain models encounter many difficulties in UI UX in interaction between Layer 1 with each other.
So Blockchain is constantly developing and upgrading, there are two clear trends: improving and updating old Monolithic Blockchains by creating new Monolithic Blockchains like Aptos or choosing a completely new path like Modular Blockchain like Celestia.
The faster Monolithic Blockchains want to speed up, the higher the node’s hardware requirements need to be. The higher the hardware requirements, the higher the rebuilding cost, which makes few people dare to spend money to build nodes, so causing the network to lose its decentralization.
Modular Blockchain separates the stages like this, requiring lower hardware, but the transaction speed is not guaranteed to be as fast as Monolithic Blockchain or not?
Typical Models for Modular Blockchain
Ethereum 2.0 with Sharding and Layer 2
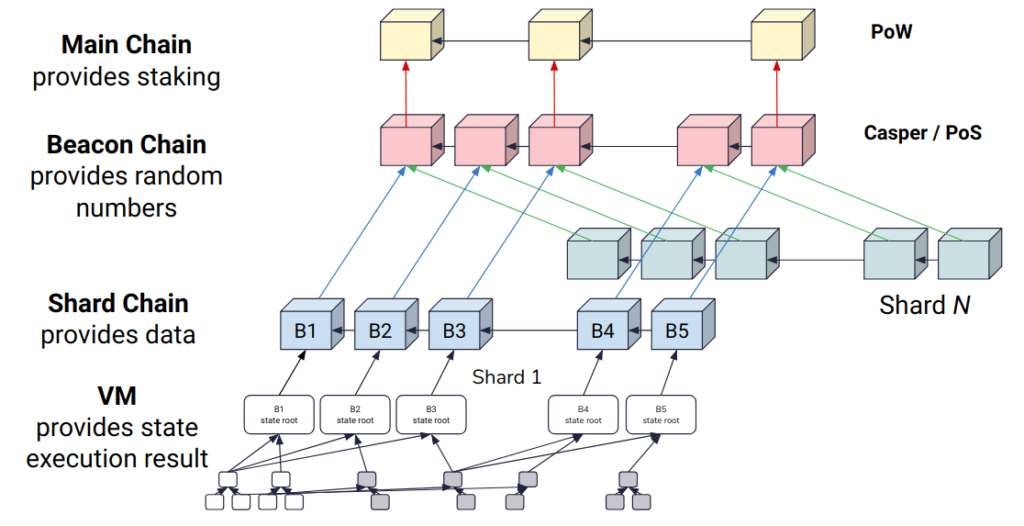
With the model between Ethereum and Layer 2
Transactions will take place and be executed on Layer 2, then the transactions will be packaged into a Block and accompanied by a transaction proof that is then sent to Ethereum for Consensus and Data Storage. .
Here you can clearly see that Execution has taken place on Layer 2 and the remaining factors such as Dispute Resolution, Consensus or Data Storage are on Layer 1, this is how a Modular Blockchain works.
Ethereum 2.0 with DankSharding
When Ethereum completes its roadmap, Ethereum will successfully integrate Sharding to solve scaling problems. Sharding will have many different applications with Ethereum. Ethereum will have many shard chains, each shard chain will be in charge of a different group of validators.
To put it simply, in a certain period of time, a blockchain can only process 1 transaction, but with shard chains, these chains will independently process transactions, so the more shard chains, the greater the number of transactions. processed at the same time is even higher.
The way Shard Chains work is quite similar to Layer 2 where Execution will take place on the Shard Chain and Consensus and Data Storage will take place on the main chain.
It can be said that in the future Ethereum will become a comprehensive Modular Blockchain instead of currently being part Monolithic and part Modular.
Celestia – Leading the Movement of Modular Blockchain
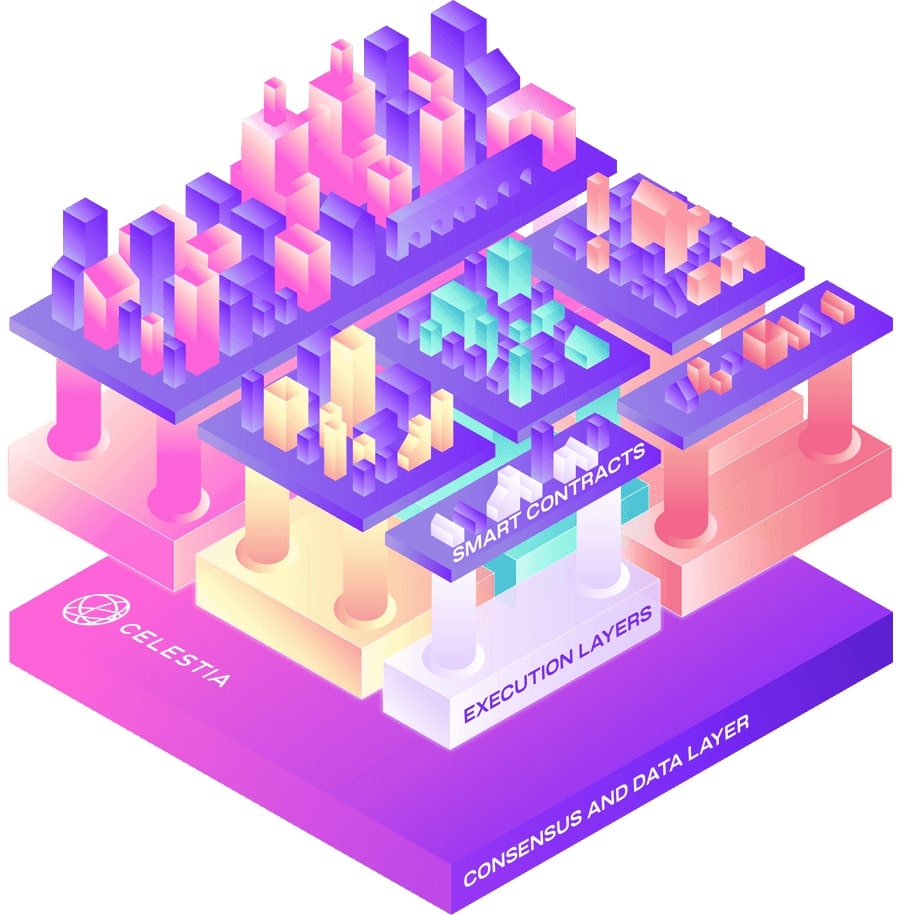
Celestia’s model is quite similar to the model of Ethereum and Layer 2. Celestia will divide the elements surrounding a transaction into 2 different layer 2: Execution Layer and Consensus & Data Layer.
Execution Layer is where transactions are executed.
Consensus & Data Layer is the place for Consensus and Data Storage.
Celestia aims for a bigger future when any blockchain platform can integrate and use Celesia as a Consensus & Data Layer, so Celestia’s direction is both B2B and B2C. I am also very excited about what Celestia will deploy in the near future.
Challenges of Modular Blockchain models
- This is a model that has been proven to be effective for the operating model between Ethereum and Layer 2, but currently there is no fully modularized blockchain, so there are still risks over time. implementation and initial period of operation.
- Obviously, Modular Blockchains will face many more technical challenges than regular Monolithic Blockchains.
- Because it has not been officially deployed, it is not possible to guarantee 100% that this will effectively solve outstanding problems with Monolithic Blockchain.
- For Celestia, if they determine to follow B2B direction, the amount of data stored on Celestia is increasing, will it push up the storage price on Celestia, thereby increasing the transaction fee on Celestia?
Summary
Modular Blockchain is still very new to the crypto market but it is considered a new breeze in the crypto market in particular and the entire blockchain industry in general. The challenge is still there, but projects, especially Celestia, are very focused on building the first full Modular Blockchain in the crypto market.


