What are Taproot Assets? Taproot Assets is a protocol that helps issue assets on the Bitcoin network, and can be moved through BTC’s second layer Lightning Network. So what is special about this protocol? Let’s find out through the article below.
To better understand the project, people can refer to some of the analysis articles below:
- What is Bitcoin? All About Bitcoin
- What is State Channel? State Channel Solution Overview
Taproot Assets Overview
In the history of BTC, there have been many proposals related to bringing assets to the BTC network. With its design, Taproot Assets can migrate assets to BTC and Lightning in a more private and scalable way.
Taproot Assets (formerly Taro) is a protocol that helps issue assets on the BTC network, which can be exchanged through BTC’s second layer Lightning Network with high speed and low cost. The core of Taproot Assets can be understood as exploiting the security and stability of the BTC network while inheriting the speed, scalability, and low cost of the Lightning Network. Taproot Assets is a protocol developed by Lightning Labs.

What are Taproot Assets?
Taproot Assets helps users issue all types of assets on BTC such as Stablecoins, Shares, Tickets, “ownership rights”, or works of art without technical barriers.
The assets use Taproot Assets scripts, which allows them to perform many of the same functions as BTC. Currently, Lightning Labs is focusing on stablecoin development.
Mechanism of Action
Taproot Assets are formatted as BIP 341. Taproot Assets use Merkle and Taptweak trees to commit information that identifies asset creation and ownership.
Taproot Assets can be transferred on-chain, or using open Lightning Network channels. To release assets and transfer them, Bitcoin transactions need to be created. This requires users to have BTC to pay transaction fees. Each asset created also requires a small amount of satoshis.
Users who create assets can create rules surrounding that type of asset. They can limit the total supply, or leave it unrestricted to develop for future purposes.
Taproot assets are deposited into the Lightning Channel to execute transactions.
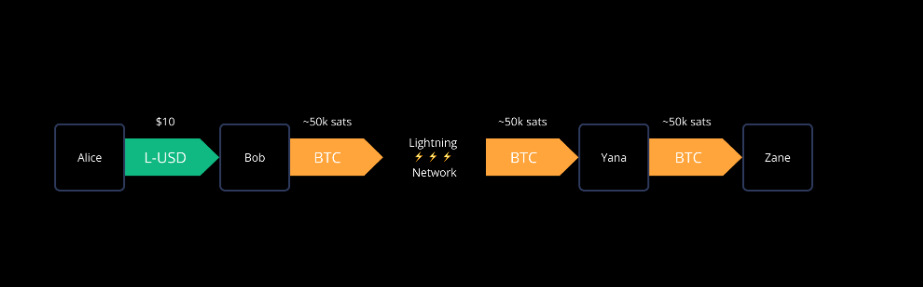
Use Lightning Channel
Main Structure
Taproot Assets are formatted as BIP 341. Taproot Assets use Merkle and Taptweak trees to commit information that identifies asset creation and ownership.
Taptweak
When a Transaction is added to a Block, it must be committed and cannot be edited or changed. To ensure data authenticity, Lightning Labs uses a technique called Taptweak that allows them to selectively reveal data without revealing the private key.
Sparse Merkle Tree
Sparse Merkle Tree SMT is a data structure where it can prove that a particular type of data does not exist within its structure. SMT is a repository of authenticated data. SMT allows users to check the authenticity of a type of data without having to download the entire data.
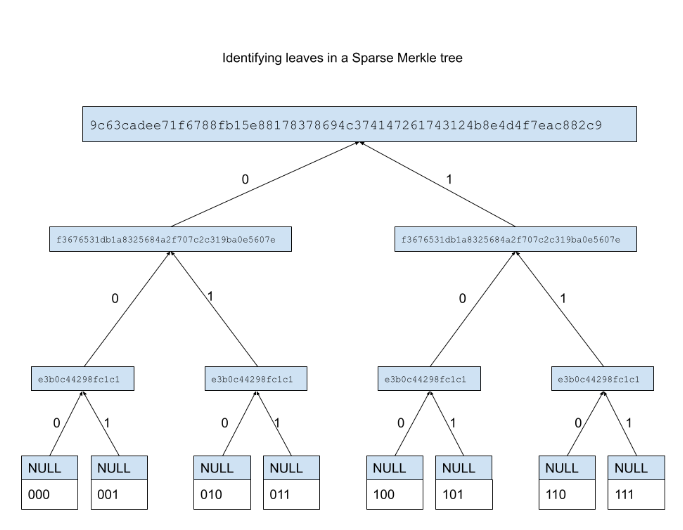
Structure of SMT
Merkle Sum Trees MST
MST enables efficiency in verification by committing to the quantity of value.
Highlights of Taproot Assets.
Assets released on Taproot can be deposited into Lightning Network channels, where nodes can provide conversions from BTC to Taproot Assets. This allows Taproot Assets to interact with the Lightning Network more fully.
Taproot Assets participants who transfer assets are subject to a verification and storage fee. Information will be stored off-chain in warehouses called “Universes”.
Some highlights of Taproot Assets include:
- User-friendly: Low verification fees and only need to connect to BTC trading. The protocol does not require knowledge of the entire blockchain industry.
- Taproot Assets enables the exchange between assets and BTC.
- Taproot Assets can release both unique assets as well as collections
- Taproot Assets channels can be created alongside BTC channels, allowing the protocol to leave the Lightning Network without consuming any additional resources. For example: Duy can create 2 channels with Dung in one BTC transaction. Of which, 1 channel for assets, 1 channel for BTC.
- The future will include the Zero-Knowledge mechanism as part of the TaprootAsset transaction.
How to Release Assets
To release assets on Taproot Assets, people follow these steps:
Step 1: Create Assets ID
To release assets, users need to identify them. They generate a 32-byte Assets ID created by hashing the following three factors:
- The outpoint: used to mint assets.
- An assets tag: Used to classify assets, customize factors depending on the mint.
- Meta Information: Information such as links, photos, videos, downloads.
Step 2: Assets script
Assets script helps the protocol know who the asset will be for and how much. Taproot Assets allows users to create multiple assets in a single transaction, however those asset types must have their own different parameters.
Step 3: Assets leaves
Each leaf will include type, value, and length (TVL: type, value, length). It includes information such as version, asset ID, quantity, as well as data related to previous transfers of this asset type. For example: signature.
Step 4: Create Sparse Merkle Sum Tree
Creating a PMS tree helps issuers manage assets. Each account is identified by its key (256-bit). And each leaf (Assets Leaves) of the tree will include information related to the amount of assets that account is holding.
Step 5: Release assets
Once Taproot Assets publishes a transaction and is confirmed in the bitcoin blockchain, there is no reversing the asset creation.
Application Of Taproot Assets
Currently the protocol is supporting users to create assets on the BTC network and can be traded through Lightning channels. However, the most obvious application that the community as well as Lightning Labs is aiming for is the development of stablecoins and payments.
Summary
Taproot Assets is opening up new avenues in exploiting the potential of the BTC network. Issuing assets will help the BTC network have more applications in the future, thereby increasing its value. Through the article, I hope everyone has an overview of the protocol as well as the question of what Taproot Assets is.


