What is DVT? DVT stands for Distributed Validator Technology, a technology that helps improve security and decentralization on the Ethereum network. So what are the outstanding projects in the DVT segment or what is it about DVT that attracts investors? Let’s find out together in the article below.
To better understand DVT, people can refer to some of the articles below:
- Lido V2 Review: Towards a Perfect DeFi Protocol
- What is Ethereum? All About Ethereum
- What Are Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSD)? Top 5 LSD Projects with Great Growth Potential
Overview of DVT Technology
What is DVT?
DVT stands for Distributed Validator Technology, roughly translated as Distributed Validator Technology, which is a security support method for Validators by distributing and sharing responsibility for keyphrase management and transaction signing for multiple parties. different from that to reduce errors, increase the recovery ability of Validator itself and have many positive impacts on Ethereum in the future.
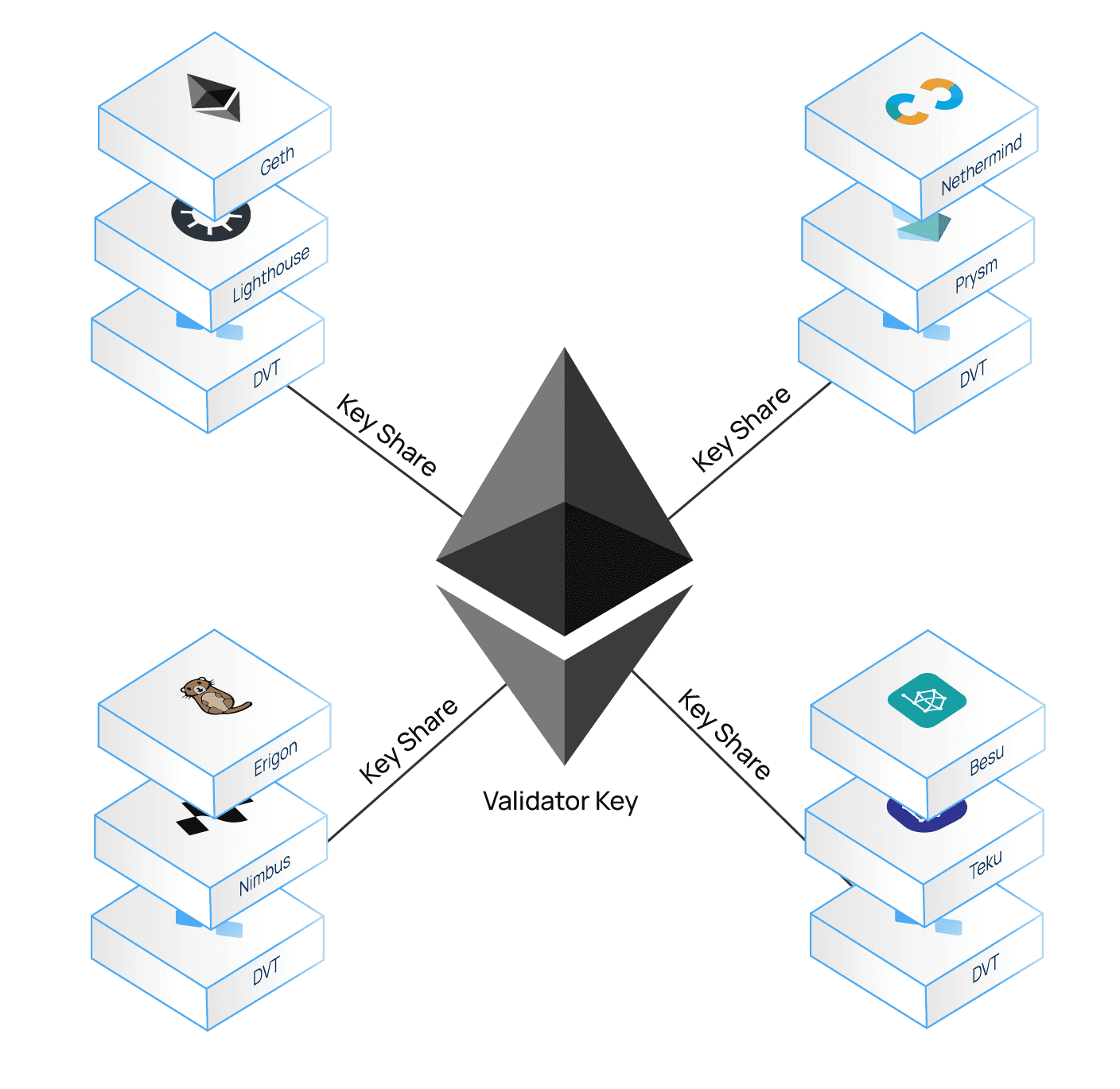
Simply put, to operate a Validator, the Node Operator must own a wallet with 12 or 24 characters and then use this wallet during operation and signing transactions on the Ethereum network. However, this makes it so that if that Validator is attacked and the attacker can take away the Node Operator’s Keypharse from which their entire assets are stolen and if it happens on a large scale then the entire network. Ethereum may be in trouble. That’s why DVT technology was born.
DVT technology allows the Keypharse or Private Key to be split into many different segments and stored on many different computers called a cluster. Of course, the Private Key is not fully stored on any computer, thus allowing hackers to successfully attack a computer and not be able to do anything to the Node Operator. Besides, some computers going offline does not affect the network because only a subset of a cluster signs, transactions can still take place as usual.
Why Ethereum needs DVT technology
Security: Protect assets
Validators upon initialization will establish a Public & Private Key pair in which Validator Keys are used to participate in the consensus process and Withdrawal Keys are used to withdraw funds. In the context that Withdrawal Keys will be stored securely, Validator Keys must always be online 24/7. If the Node Operator has a problem leading to the Private Key being stolen by Hackers:
- Hackers can control Validator and can then take bad actions, stop working,… leading to Validator being fined by the network’s existing regulations.
- Hackers can take away Node Operator’s ETH.
DVT solves this problem through some basic steps as follows:
- The Node Operator’s Private Key will be encrypted.
- The Private Key will be divided (can be understood as cut) into many different segments. Each of these segments is called Key Shares.
- These Key Shares will be distributed to many different nodes on the network.
- These nodes will join together to perform the work of a Validator.
This factor helps users to keep their Validator Keys offline in an extremely safe and secure way.
No Single Points of Failure
Dividing the Validator among multiple operators and miners allows the Validator to withstand individual hardware and software failures without worrying about being offline, thereby leading to penalties. Visualize it in an easy-to-understand way like:
- If the Validator is just a single piece of hardware, it is likely that it will occasionally encounter an error that will lead to the Validator being offline and penalized.
- If the Validator is shared among 20 different sets of computers, then in reality only 10 – 12 computers (for example) can operate the Validator. If in a bad case there are 4 – 5 computers with hardware or software errors, Validator can still operate normally.
Decentralized: Decentralized
The current market context will have a few large Validators taking over the work and rewards of smaller Validators. Even though being this big requires a lot of effort, money, people, etc., it also affects the decentralization of the network. But with DVT technology, even large Validators can be divided into smaller nodes.
Thanks to DVT technology, large Validators can still exist without affecting the decentralization of the network.
In summary, DVT technology brings clear benefits such as:
- Brings decentralization to the network without major changes.
- Minimize trust in authentication operations.
- Ensuring the vitality of the network.
- Improve network diversity.
- Enhance security for Noda Operators or Validators.
Mechanism of operation of DVT technology
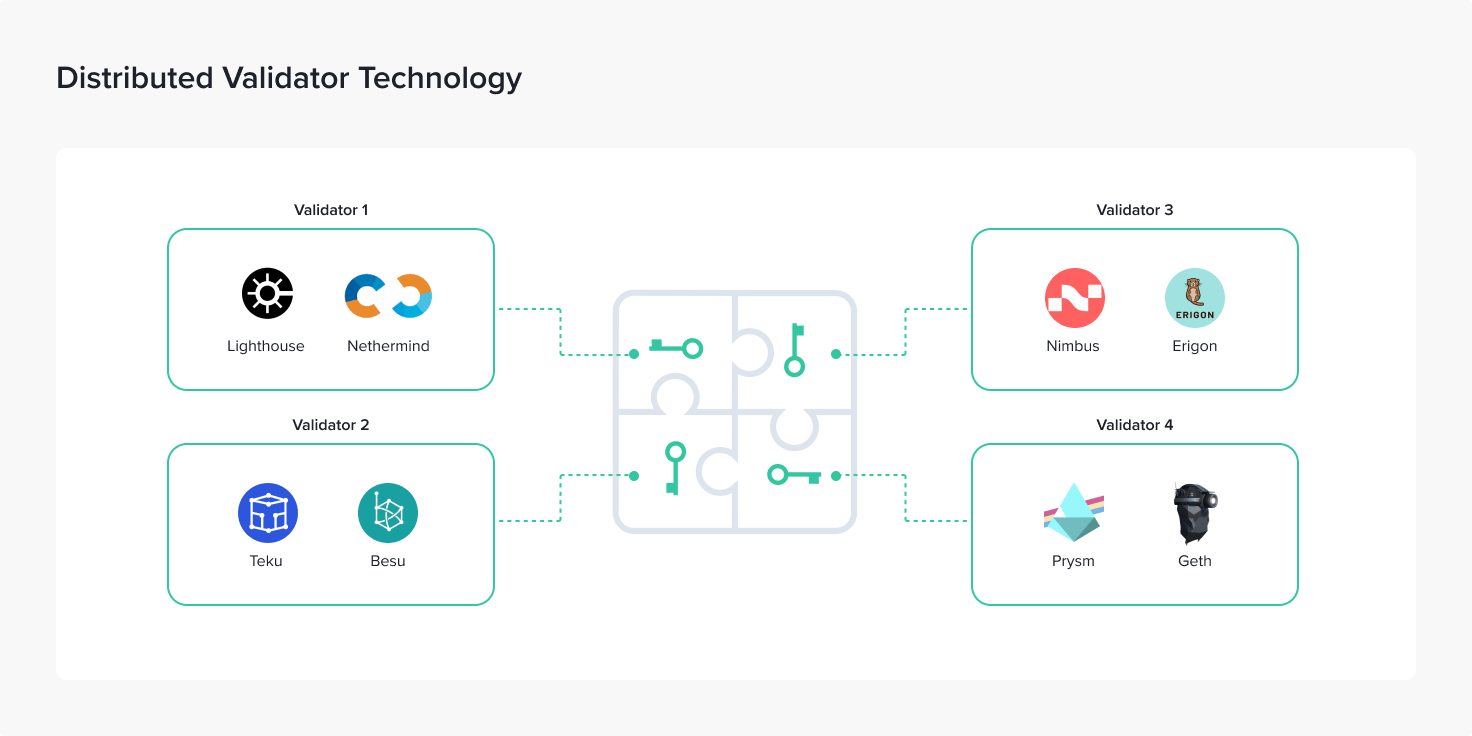
In order for DVT technology to work, it includes many components such as:
- Shamir’s secret sharing: Validator will use BLS Key.
- Threshold signature scheme: Determine the number of votes to sign. For example: Only 5 computers need to sign for the transaction to be approved.
- DKG: The process of encrypting and generating Key Shares, followed by distributing Key Shares to different computer clusters.
- MPC: Validator Key will be secretly generated using multi-party computation. From there, any Node Operator can never fully know the Validator Key but can only know its Key Shares.
- Consensus Protocol: Consensus Protocol will select a node as the block proposer. That node will share the block with the nodes in the cluster, then the block will be signed by the nodes in the cluster. Reaching the minimum number as in the Threshold signature scheme section, the block will be proposed on Ethereum.
Applications of DVT Technology
DVT technology allows a number of new areas to emerge such as:
- Staking Solo: Allows single users to participate in staking without spending money on hardware and keep it running.
- Staking As a Service: Node Operators can use DVT technology to limit their risks. DVT technology helps manage many different nodes through a single key, thereby saving operating costs.
- Staking Pool: With DVT technology, trust in each other is reduced to a minimum, so everyone can safely and securely deploy a Staking Pool together.
Some Disadvantages of DVT Technology
Although there are many advantages, DVT still has some disadvantages as follows:
- Latency: If there is only 1 Validator operating independently and 1 Node cluster also operating a Validator, a cluster will certainly have more latency than a Validator.
- Expense: Also stemming from the above reasons can increase operating costs. However, it reduces costs in other stages.
- Need to decentralize soon: Having few DVT Clinet also makes it vulnerable to Hacker attacks
Summary
DVT technology brings a breakthrough to security and decentralization on Ethereum, so this will be one of the core technologies of Ethereum in the near future.
Hopefully through this article, everyone can understand more about what Distributed Validator Technology DVT is?


