In the DeFi market, there are two most basic types of asset trading mechanisms: AMM-based and Order Book-based. From these two basic mechanisms, many different variations have been developed. In this article, we will learn about CLOB – Central Limit Order Book, a transaction matching model that early protocols like dYdX brought from the traditional financial world of TradFi into DeFi.
To have an overview of the content of the article, you can refer to the following articles:
- What is Decentralized Exchange (DEX)? The Role of Decentralized Exchanges in DeFi
- What Are Derivatives? Powerful Profit Tool for Crypto Winter
- What is dYdX? dYdX Cryptocurrency Overview
- Series 10: Crypto Unlock | dYdX Layer 1 Becomes Derivatives Exchange on Cosmos Ecosystem
What is Central Limit OrderBook?
The Central Limit Order Book can be called Centralized limit order book, is a transaction matching model between buyers and sellers in a market. This is the method used by almost all centralized exchanges in the crypto market and in TradFi.
CLOB is applied to both spot and derivative transactions.
Structure of an order book
When traders want to buy or sell assets on the exchange, they must make a pending order (limit order). This order is recorded in the order book (OrderBook) including information about the bid or ask price, along with the buy or sell volume of the order.
An order book is a list that aggregates and lists buy and sell orders for the same asset. These orders are arranged sequentially according to price levels surrounding the current price of that asset. Below are a few illustrations of order books that are very familiar to CEX users or stock traders:
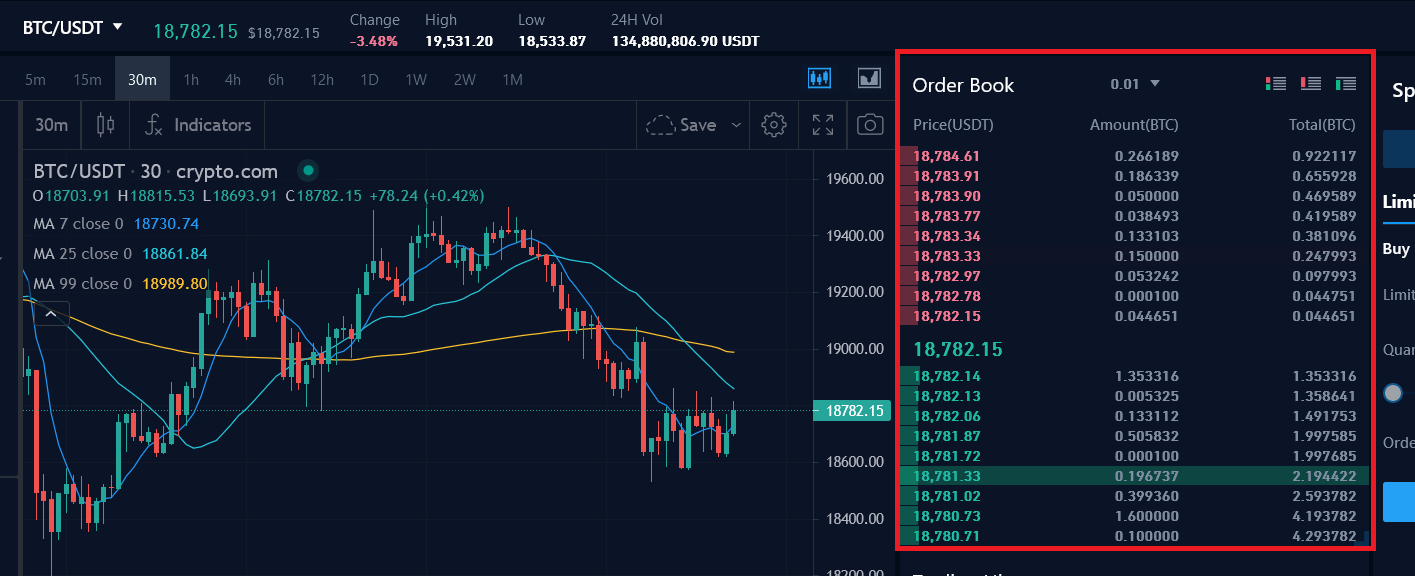
With the order book model, the price of the traded asset will be the lowest offered price on the Orderbook. In other words, the current price of the asset is the price Ask, that is, the lowest price at which people are willing to sell assets to others in the market. Conversely, the highest price a trader is willing to pay to buy that asset is called the price Bid.
Usually, the order book will list sell orders in ascending order by price from the Ask price, located at the top of the order book, and list sell orders in descending order by price from the Bid price. , located in the lower half of the order book.
The difference between the Bid and Ask prices is called Bid-Ask Spreadin fact it is often referred to as Spread. This difference always exists and it is beneficial to the exchange, directly bringing revenue to the exchange. With the BTCUSDT trading pair and parameters as shown above, an example can be given as follows:
- If person A buys BTC with USDT on crypto.com, this person will have to buy at the lowest price of 18,782.14 USDT per BTC. If that person wants to sell immediately, the selling price must be 18,782.14 USDT per BTC. That is an immediate loss of 0.01 USDT per BTC.
Spread can be considered a hidden fee that users are required to accept when trading on an exchange using OrderBook.
In addition, with the order book model, all matched transactions will be recorded in the transaction history, with information about matching time, matching price, and matching volume.
Order Matching System
Order Matching System, Matching System or Matching Engine are common names for order matching systems. Basically, the order book is a tool for arranging orders, and the matching engine is responsible for matching buy orders and sell orders together. An exchange that uses order books must also have a matching engine.
Matching engines differ in the algorithms they use to match sales transactions. The two most popular algorithms are FIFO and pro-rata.
Limit-stop/pending orders and market orders
The Order Book model allows traders to execute all types of orders, which are divided into two main types: pending order and market order.
A market order is very simply a trading order that will be executed immediately, at the lowest price in the market that has sufficient liquidity to match the requested volume.
For example: A person wants to buy 1 BTC with market order matching mode when the price of Bitcoin on the exchange is currently 18,000 USDT per BTC. This buy order will be matched with one or more other sell orders at the same price of 18,000 USDT per BTC, so that the BTC volume of both buying and selling sides is equal.
On the other hand, a pending order is an order that must wait to be executed when the market price of the asset meets certain conditions. There are two types of pending orders: limit command and stop order. The meaning of these types of trading orders is as follows:
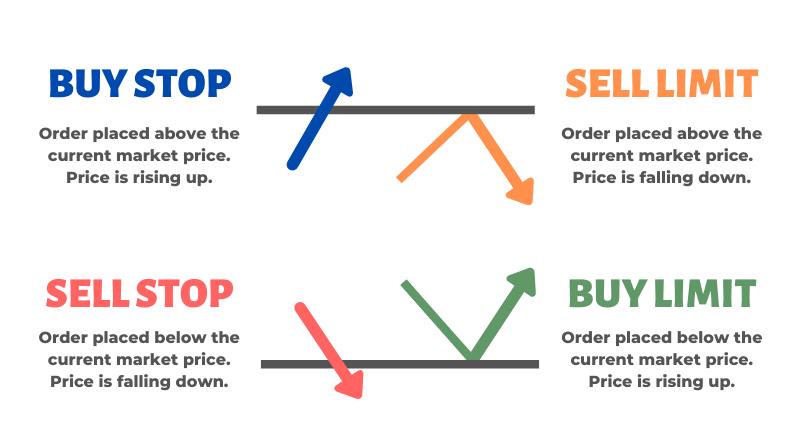
- Buy limit order: Buy order at a price lower than the market price of the asset. When the market price drops to the threshold required by the order, the order will be matched.
- Sell limit order: Order to sell at a price higher than the market price of the asset. When the market price increases to the exact threshold required by the order, the order will be matched.
- Buy stop order: Buy order at a price higher than the market price of the asset. When the market price increases to the exact threshold required by the order, the order will be matched.
- Sell stop order: Order to sell at a price lower than the market price of the asset. When the market price drops to the threshold required by the order, the order will be matched.
Above are the basic contents about CLOB. Exchanges can change the names of order book components or the names of trading order types, but they are all based on these basic foundations.
First DEX Order Book Built by dYdX
Versions V1 and V2 of dYdX are built on Ethereum. According to dYdX white paper 2017, at that time, dYdX provided two types of products: Margin Trading and Options.
At version V3, dYdX has transformed into a Layer 2 Validium of Ethereum, supported by StarkWare and only offering Perpetual trading products.
In all three initial releases, dYdX’s CLOB and matching engine were operated off-chain on servers operated by dYdX Trading Inc. and their other partners (namely Amazon Web Services – AWS) operate. That is, trading orders will be recorded in the off-chain order book, matched off-chain and managed by dYdX, while still being executed onchain. This is a trade-off between decentralization and protocol efficiency.
dYdX V4 went mainnet at the end of October 2023 and had a big change when it moved to being a Layer 1 on Cosmos. In addition, version V4 will completely decentralize the order book and matching engine. This version was introduced by dYdX in 2022 and gave birth to a variant of CLOB called d-CLOB (Decentralized CLOB) or some places call it DLOB (Decentralized Limit OrderBook).

When dYdX becomes Layer 1, validators will take on the role of operating the OrderBook. dYdX Trading Inc. will no longer have the right to participate in the process of monitoring and operating the order book. This is a big step forward in decentralizing dYdX’s model.
CLOB With AMM
In the DeFi space, CLOB and AMM have always been the two extremes in the debate about which tool is more suitable to use for decentralized trading. CLOB is applicable to spot and derivatives transactions, while AMM only supports spot transactions.
However, there are many projects that have also relied on the AMM principles of Uniswap V2 and Uniswap V3 to build Perp DEX products. You can learn about AMM in the article What is vAMM (Virtual AMM)? Overview of Virtual Automated Market Makers.
In fact, although CLOB can support spot trading, AMM DEXs are the dominant force in terms of spot trading in DeFi. This can come from many reasons, both in terms of user experience, economic model, decentralization, … etc.
However, in terms of Perpetual Trading, CLOB is still the most popular (through the case of dYdX). Currently, dYdX is still the largest Perp DEX in terms of trading volume, while in terms of TVL, it is not larger than GMX. As for Perp DEXs operating on the vAMM model (virtual AMM), they appear to be ineffective and do not attract users.
Currently the next biggest step that CLOB DEX/Perp DEX can take is to decentralize the operation of the order book. This forces these DEX/Perp DEX to follow the Application Specific-chain trend. In addition, Perp DEXs that use liquidity pools and are based on oracle prices like GMX or vAMMs like Perpetual Protocol are still continuing to research and develop products.
Conclude
Above is an overview article about CLOB as well as new variations of this trading mechanism. The Perpetual Trading game on DeFi is not over yet and we will need to look forward to the next changes.


